The field of quantum technologies, specifically quantum computers, has captivated the attention of scientists and governments worldwide. With the promise of solving problems that even the most powerful supercomputers struggle with, quantum computers are considered the future of technology. However, due to their reliance on the laws of physics different from conventional computers, ensuring the quality and reliability of quantum computers is a challenge.
A Collaborative Research Effort
Professor Jens Eisert, a physicist at Freie Universität Berlin, has headed an interdisciplinary research team that aims to address this challenge. In a recent study published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, they have developed innovative methods to test the quality of quantum computers. This breakthrough research incorporates principles from physics, computer science, and mathematics.
Quantum computers operate on the principles of quantum mechanics, utilizing individual atoms or ions as computational units. At this minuscule level, nature behaves in a drastically different manner compared to our everyday experiences. These extraordinary computers have one significant weakness – their sensitivity to interference from the environment. When a quantum computer is not adequately shielded, the qualities responsible for its computational power diminish, rendering it ineffective.
The critical question arises – how can researchers determine whether a quantum circuit has functioned correctly? Similar to safety tests conducted on vehicles, quality control processes are necessary to validate the reliability of quantum circuits. Without such methods, the results obtained from quantum computing are unreliable.
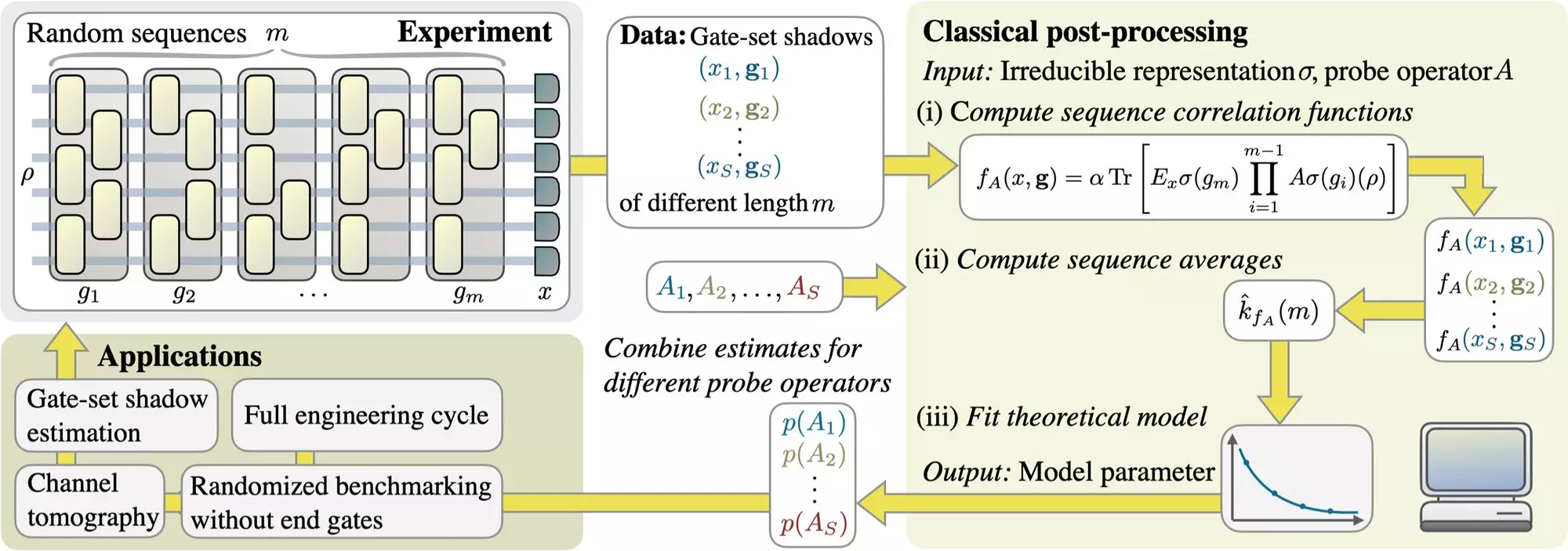
Through collaboration with various research institutions, Professor Jens Eisert’s team has devised a unique approach to test the quality of quantum computers. The process is surprisingly straightforward yet ingenious. The researchers implement random circuits, and the resulting measurement outcomes are analyzed in quantum bits or qubits – the fundamental units of quantum information. These data provide invaluable diagnostic information, enabling researchers to assess the performance of quantum gates, identify interference factors, and uncover unintended interactions.
To better grasp the concept, imagine sending your car for a comprehensive maintenance check. The researcher equates the testing process to swiftly and randomly wiping down the vehicle’s exterior multiple times, all the while assessing the engine’s functionality, the presence of washer fluid, and the proper adjustments of brakes. This approach encompasses a range of diagnostics in a single measurement, providing a holistic evaluation of the quantum computer’s quality.
The groundbreaking research by Professor Jens Eisert’s team establishes a foundation for a new verification method. This method will play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of future quantum computers integrated into technological devices. By leveraging this research, the development and application of quantum technologies can bring significant economic and scientific benefits.
As the world envisions a future shaped by quantum technologies, the quality control of quantum computers is a paramount concern. The remarkable research conducted by Professor Jens Eisert and his interdisciplinary team signifies a groundbreaking step in the right direction. By employing innovative testing methods, these pioneering scientists have proven their commitment to unlocking the full potential of quantum computing and revolutionizing the technology landscape. With their work, the era of reliable and high-quality quantum computers draws nearer, promising a future of remarkable scientific and technological advancements.

Leave a Reply