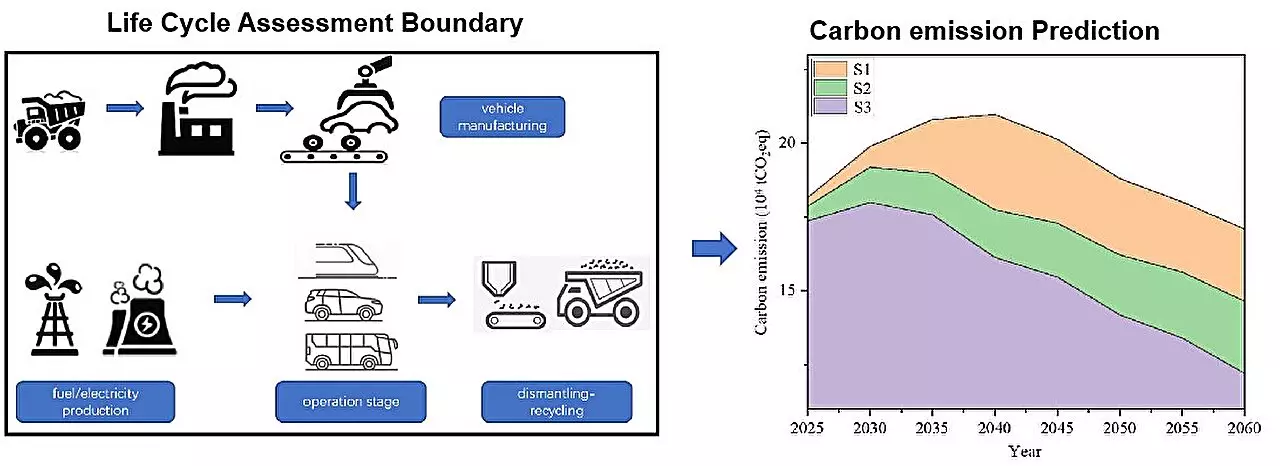
Transportation is a major contributor to global carbon emissions, making it crucial for countries worldwide to address this issue. High-speed railways (HSR) are widely considered as the future of intercity transportation due to their high degree of electrification. However, the lack of relevant data on the carbon reduction potential of high-speed rail travel and effective regulatory approaches for different transportation modes has been a persistent challenge. In a recent study published in the journal High-Speed Railway, researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University aimed to provide insights into the carbon emissions of different transportation modes throughout their entire life cycle.
The study’s lead author, Lu Yintao, explains that assessing carbon emissions throughout the entire life cycle of a product or tool provides a more accurate gauge of its environmental friendliness. To evaluate the carbon reduction potential, the researchers analyzed the entire life cycle carbon emissions of vehicles using a per-person-per-kilometer evaluation unit. This approach considers the multiple energy sources utilized by different transportation modes, such as gasoline and electricity.
Historically, road transportation, including private cars, buses, and railways, has been the main mode of passenger travel. However, the study highlights the stark differences in carbon emissions between these modes. The findings reveal that high-speed rail demonstrates a significant carbon emission reduction, with an intensity of only 24-32% compared to private vehicles and 47-89% compared to buses. This indicates that high-speed rail travel has immense potential for reducing carbon emissions and should be prioritized as an eco-friendly transportation option.
In addition to its impact on carbon reduction in transportation, the study also provides valuable information for vehicle manufacturers regarding the materials they should prioritize for production. By understanding the significant carbon reduction implications, manufacturers can focus on developing vehicles that align with sustainable practices and contribute to a greener future.
Yao Hong, the senior author of the study, emphasizes the continuous nature of carbon emissions during transportation and their role in the overall life cycle. The research aims to provide theoretical support for China’s carbon reduction efforts in the transportation sector. By analyzing the carbon emissions of different transportation modes, policymakers and regulators can make more informed decisions and develop effective strategies to promote sustainable transportation practices.
High-speed railways offer a promising solution to curb carbon emissions in the transportation sector. The ability of high-speed rail travel to significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to private vehicles and buses highlights its potential for a greener future. With a holistic understanding of the entire life cycle of transportation options, policymakers and manufacturers can prioritize sustainable practices and contribute to global carbon reduction efforts. As the world continues to focus on addressing climate change, the research from Beijing Jiaotong University plays a crucial role in guiding the future of intercity transportation towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly direction.

Leave a Reply