As humankind sets its sights on Mars, a new chapter in space exploration unfolds. The challenges posed by long-distance space travel drive the quest for faster and more efficient propulsion systems. In a groundbreaking achievement, NASA recently conducted a successful test of the Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE), pushing the boundaries of technology and bringing us closer to the Red Planet.
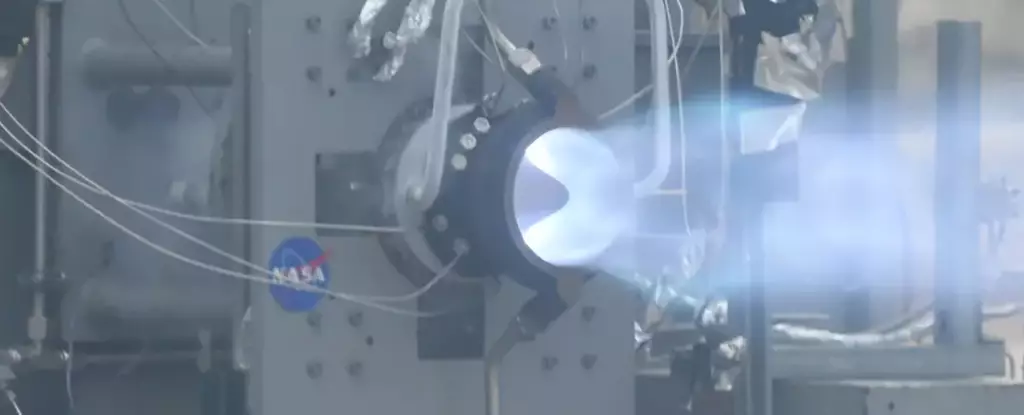
The RDRE, a prototype engine tested at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, demonstrated unprecedented thrust capabilities. It achieved an impressive 25,810 newtons (5,800 pounds) of thrust for an astounding 251 seconds. This accomplishment surpasses the previous record of 17,800 newtons for nearly a minute, which was achieved in 2022 and later validated in 2023. The ultimate goal is to develop a fully reusable 44 kilonewton class RDRE, surpassing the performance of traditional liquid rocket engines.
Leading the RDRE project at the Marshall Space Flight Center, combustion devices engineer Thomas Teasley highlights the engine’s remarkable design efficiency. The RDRE relies on a sustained detonation circling around a ring-shaped channel. A mixture of fuel and oxygen ignites with each passing explosion, propelling the spacecraft forward. This innovative approach not only enhances propulsion performance but also significantly reduces propellant fuel consumption compared to conventional rocket engines. By streamlining the machinery and mechanisms, the RDRE makes space exploration more cost-effective and opens up possibilities for venturing farther into the cosmos.
One aspect that sets the RDRE apart is its utilization of 3D printing techniques to create robust machine parts capable of withstanding extreme heat and pressure. This groundbreaking method ensures the engine’s durability and reliability in the harsh conditions of space travel. Furthermore, the recent test has provided valuable insights into scaling and adapting the combustor to support various levels of thrust, engine systems, and mission requirements. With each technological advancement, NASA draws closer to its ambitious vision of sending the first astronauts to Mars in the 2030s.
Although traveling to Mars and establishing a sustainable presence on the planet pose significant obstacles, the development of an efficient propulsion system represents a major breakthrough. The RDRE’s leap in performance brings us one step closer to achieving NASA’s Moon to Mars vision. The lightweight propulsion system enables the transportation of larger payloads and masses deeper into space, expanding our exploration capabilities. With reduced costs and enhanced propulsion, the RDRE paves the way for a future where long-distance space travel becomes a reality.
NASA’s successful test of the Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine showcases the remarkable progress made in space propulsion technology. The RDRE’s innovative design, employing sustained detonation, heralds a new era in fast and efficient transport across the solar system. With reduced fuel consumption and simplified machinery, the engine revolutionizes space exploration, making it more accessible and economically viable. As we gaze towards Mars, the RDRE brings us closer to the stars, igniting our collective passion for the boundless wonders of the universe.

Leave a Reply