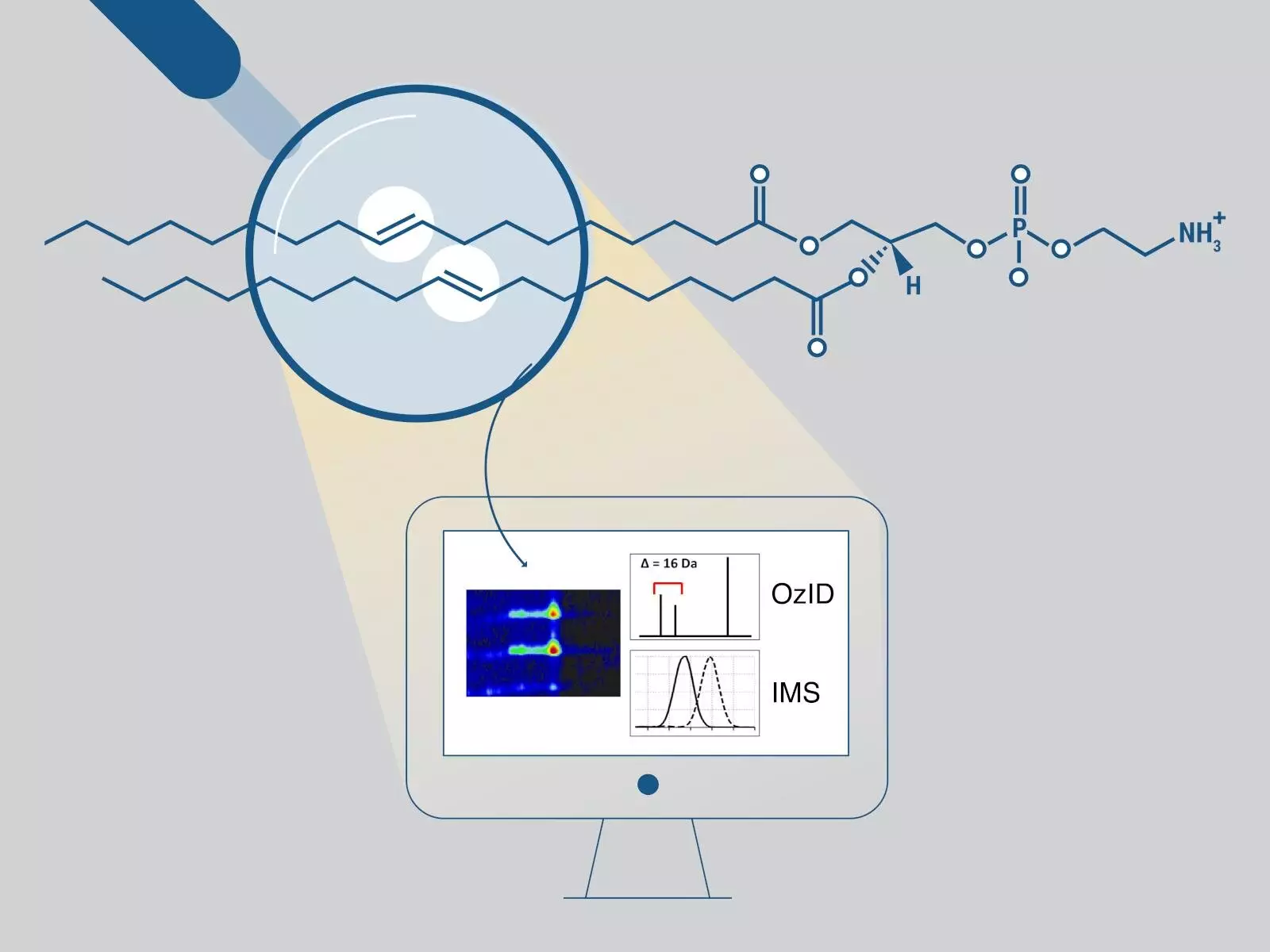
Lipids, a class of biomolecules, play a crucial role in various cellular processes. The study of lipids, known as lipidomics, is important in understanding complex biological systems. However, the challenge lies in connecting the different structures of lipids with their biological functions. One key factor in lipidomics is determining the positions of double bonds within fatty acid chains, as they can impact cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways. Unfortunately, this information is often omitted in lipidomics studies due to the complexity of obtaining and analyzing the data. To address this limitation, scientists at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) have developed a streamlined workflow called LipidOz, which combines automation and machine learning to determine the positions of double bonds.
LipidOz offers researchers a more efficient and accurate method for lipid characterization. The traditional analysis methods can determine the fatty acyl chain lengths, the number of double bonds, and even the position of fatty acyl chains (sn position). However, determining the positions of carbon-carbon double bonds has been a challenge. To overcome this, the PNNL scientists utilized a gas-phase oxidation reaction called ozone-induced dissociation (OzID), which produces distinctive fragments. These fragments provide insights into the positions of double bonds. However, analyzing the data obtained from this reaction is complex and repetitive, making it a time-consuming process with limited software support.
To simplify and automate the analysis of OzID data, the scientists developed LipidOz, an open-source Python tool. This tool seamlessly combines traditional automation techniques with deep learning approaches. LipidOz can automatically determine and assign the double bond positions of lipids. This advancement allows researchers to confidently analyze standard lipid mixtures and complex lipid extracts, enabling the practical application of OzID for future lipidomics studies.
LipidOz represents a significant step forward in lipidomics research. By providing a streamlined workflow and automated analysis, LipidOz removes the barriers that previously hindered the determination of double bond positions. This allows researchers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of lipids and their impact on cellular processes. By accurately characterizing lipids, scientists can unlock valuable insights into various biological systems and diseases.
The development of LipidOz paves the way for future advancements in lipid analysis. By combining automation and deep learning, LipidOz streamlines the process, reducing time and effort while increasing accuracy. Furthermore, as an open-source tool, LipidOz encourages collaboration and the exploration of new techniques in lipidomics research. With continued development and refinement, LipidOz has the potential to revolutionize the field of lipid analysis, enabling breakthrough discoveries and advancements in the understanding of complex biological systems.
The introduction of LipidOz by the scientists at PNNL marks a significant advancement in lipidomics research. By addressing the challenge of determining double bond positions, LipidOz offers researchers a more efficient and accurate method for lipid characterization. Through the combination of automation and deep learning, LipidOz streamlines the analysis process, enabling the practical application of OzID for future lipidomics studies. This innovation opens up new possibilities for understanding the role of lipids in cellular processes and diseases, propelling the field of lipidomics towards groundbreaking discoveries.

Leave a Reply