Peptides, short strands of amino acids, have gained significant attention in various fields such as therapeutics, biomaterials, and chemical and biological research. The ability to modify and label peptides with functional molecules is crucial for their application in these areas. One particular challenge faced by researchers is the selective attachment of functional molecules to the N-terminus of peptides without disrupting their structure and function.
Traditionally, attaching functional molecules to peptides, especially at the N-terminus, has been a challenging task due to various limitations. However, researchers from Tohoku University and Chuo University have developed a groundbreaking chemical reaction that allows the specific attachment of two distinct functional molecules to the N-terminus of a peptide containing a glycine amino acid. This innovative approach was published in the January 28, 2024, issue of the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
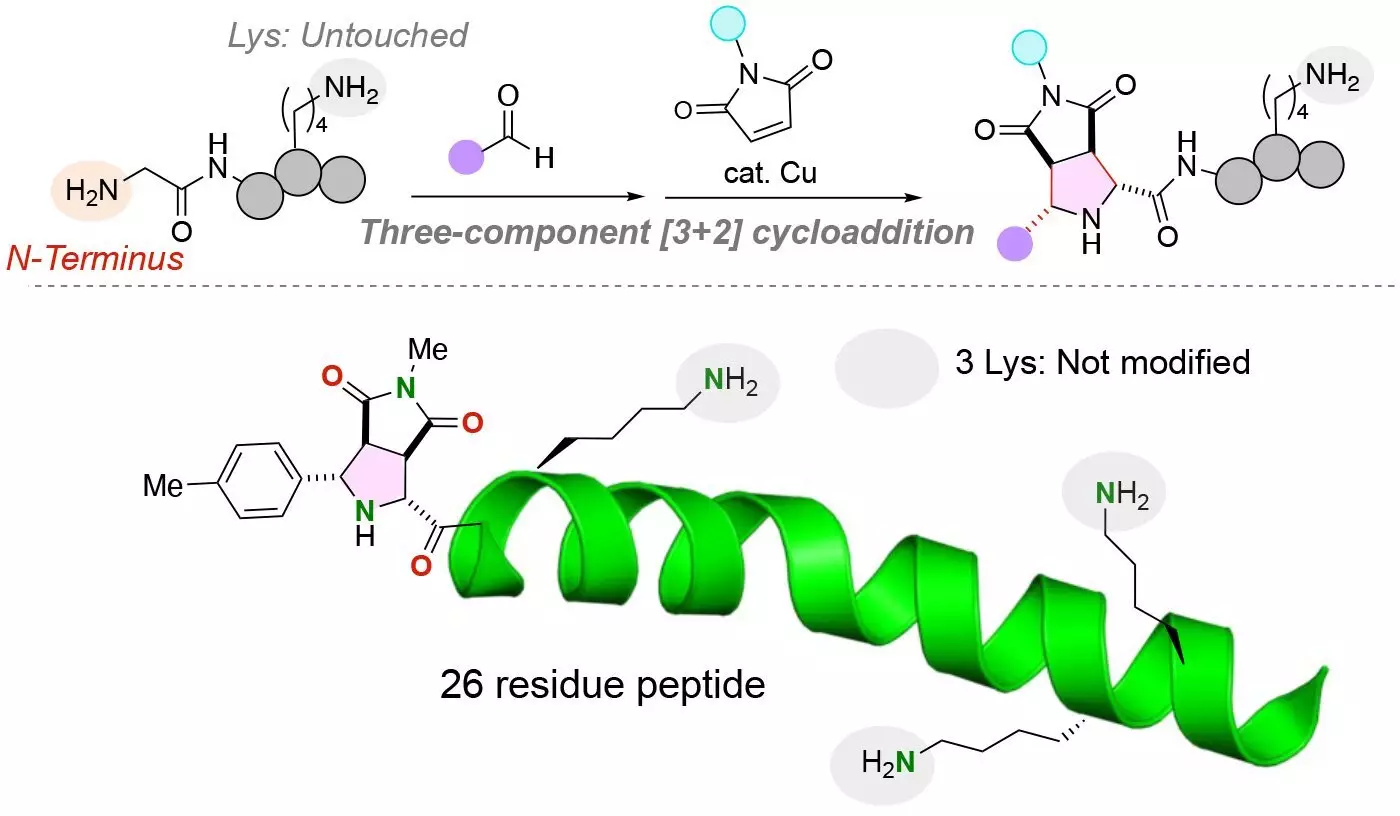
The novel chemical reaction developed by the research team enables the precise modification of the N-terminus of peptides, even in the presence of highly reactive lysine residues. This method ensures that functional molecules are attached exclusively to the N-terminus, resulting in structurally uniform conjugates with high yields. By using a copper catalyst in a three-component reaction involving peptides, aldehydes, and maleimides, the researchers achieved the simultaneous installation of two functional molecules into the peptide.
Lysine amino acids present a significant challenge when attaching functional molecules to the N-terminus of peptides due to their amine group, which can compete with the N-terminus amine group. However, the developed chemical reaction specifically targets the N-terminus amine group, even in the presence of lysine residues. This breakthrough allows for the efficient labeling of peptides with functional molecules, paving the way for diverse applications in peptide modification.
The research team demonstrated the versatility of their novel reaction by optimizing the attachment of functional groups to various di-, tri-, and oligopeptides. This highlights the potential utility of the reaction in labeling diverse peptides and larger proteins for purposes such as purification, detection, and therapeutic development. Subsequent studies will focus on evaluating the biological activity of peptides modified using this innovative approach and expanding its application to larger peptides, proteins, and antibodies for advancements in drug delivery.
The development of a site-selective dual modification protocol for peptides represents a significant advancement in the field of peptide modification. The ability to attach functional molecules to the N-terminus of peptides with precision and efficiency opens up new possibilities for research, therapeutics, and beyond. The innovative chemical reaction devised by the research team holds promise for shaping the future of peptide modification and drug delivery technologies.

Leave a Reply