Fuel cells have gained attention as a promising carbon-free energy source due to their ability to directly convert the chemical energy of fuel into electricity. Consisting of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte, fuel cells play a crucial role in the global transition away from fossil fuels.
While the operation of fuel cells results in water as the sole byproduct, the presence of water can impact the performance of the fuel cell. The reaction of water with the platinum catalyst on the electrode can lead to energy losses, hindering the efficient catalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR).
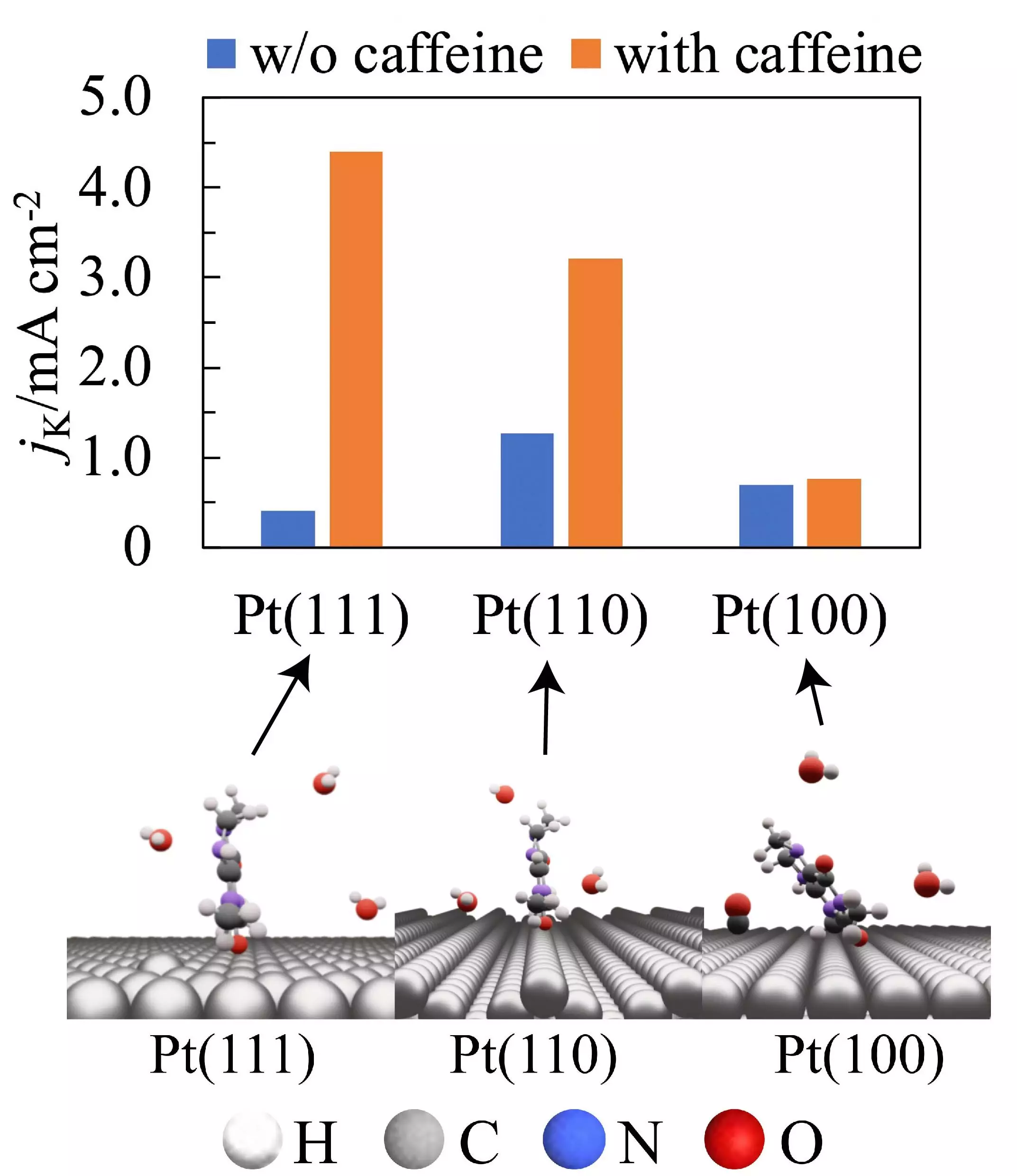
In a recent study conducted by Professor Nagahiro Hoshi and his team from the Graduate School of Engineering at Chiba University, Japan, the addition of caffeine to certain platinum electrodes was found to enhance the activity of the ORR. This discovery has the potential to reduce the platinum requirements of fuel cells, making them more cost-effective and efficient.
Experimental Findings and Results
Researchers observed a significant improvement in the electrode’s ORR activity with an increase in the concentration of caffeine in the electrolyte. Caffeine was found to adsorb onto the electrode’s surface, effectively preventing hydrogen adsorption and the formation of Pt oxide, thus enhancing the overall efficiency of the fuel cell.
Effect of Caffeine on Different Platinum Surfaces
The impact of caffeine on the ORR activity varied depending on the orientation of the platinum atoms on the electrode’s surface. While Pt(111) and Pt(110) surfaces showed a considerable increase in activity with the addition of caffeine, the effect was minimal on the Pt(100) surface due to steric hindrances.
Implications for Fuel Cell Design and Applications
Unlike traditional batteries with limited lifespans, fuel cells can continue to generate power as long as fuel is supplied, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The incorporation of caffeine to enhance the efficiency of fuel cells has the potential to revolutionize their design and increase their widespread use in various industries.
Overall, the research conducted by Professor Nagahiro Hoshi and his team sheds light on the positive impact of caffeine on fuel cell efficiency. By addressing the limitations associated with platinum requirements and water interference, the study opens up new possibilities for the development and application of fuel cell technology in a sustainable and cost-effective manner.

Leave a Reply