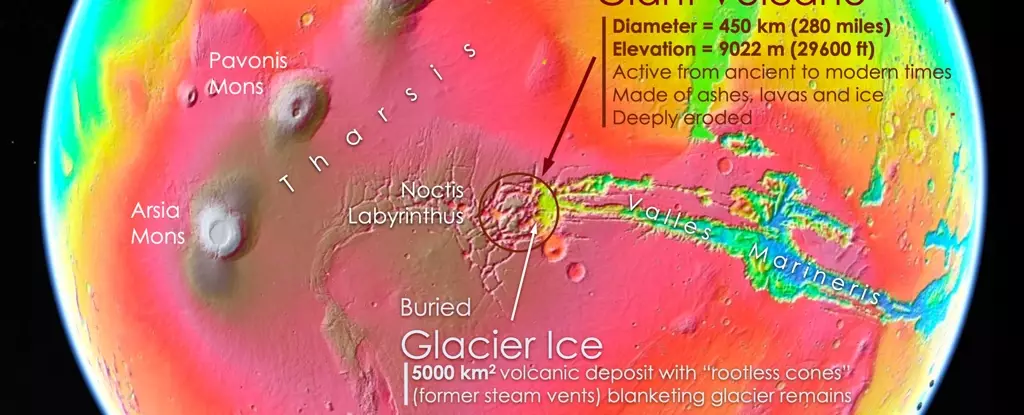
Exploring the mysteries of Mars has always been a fascinating subject for scientists. In a recent discovery, researchers have unearthed a massive, ancient volcano hidden beneath the region known as Noctis Labyrinthus. This finding has sparked new interest in the equatorial site as a potential location for uncovering clues about the planet’s past, particularly in the search for signs of ancient life.
Led by planetary scientist Pascal Lee of the SETI Institute, a team of researchers stumbled upon the hidden volcano while investigating traces of an ancient glacier in the area. Despite its heavily eroded appearance, the volcano, provisionally named Noctis Mons, stands over 9,000 meters tall and spans 250 kilometers at its base, making it the seventh highest elevation feature on Mars. The presence of a caldera, mesas, and volcanic deposits in the region all point to the volcanic nature of the mountain.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the discovery is the presence of blister-like mounds at the base of the volcano, believed to be rootless cones formed by volcanic activity interacting with underlying ice or water. This finding aligns with previous evidence of glacial ice in the region, suggesting that a sheet of glacier ice may be buried under Noctis Labyrinthus, shielded by a layer of volcanic rock. The interaction of warmth and water could create conditions conducive to the emergence of life on Mars.
The unique landscape of Noctis Mons is believed to be the result of long-term thermal erosion, glacial erosion, and fracturing processes. The canyons that dissect the volcano are thought to have formed from glaciation, further highlighting the interplay between volcanic activity and ice in shaping the Martian terrain. Satellite imagery offers a glimpse into the geological history of the region, although much remains unknown about what lies beneath the surface.
The discovery of Noctis Mons presents a wealth of opportunities for scientific exploration. Its ancient and deeply eroded nature provides a platform for studying Mars’ evolution over time, while the history of heat interacting with water and ice makes it a promising location for astrobiological research. The potential presence of remnant glacial ice near the surface in an equatorial region adds to the allure of the site for future robotic and human exploration missions.
The secret of Noctis Mons on Mars offers a tantalizing glimpse into the planet’s geological and potentially biological past. The discovery of the hidden volcano and evidence of glacial ice underscore the complexity of Mars’ history and raise exciting possibilities for future exploration efforts. By unraveling the mysteries of Noctis Labyrinthus, scientists may ultimately shed light on the ancient secrets of the Red Planet.

Leave a Reply