The recent hailstorm that hit Gerona, north-eastern Spain on 30 August 2022 was no ordinary event. Individual hailstones as large as 12cm were documented, causing widespread damage to buildings, cars, and agricultural areas. The severity of this hailstorm resulted in 67 injuries and tragically, one fatality.
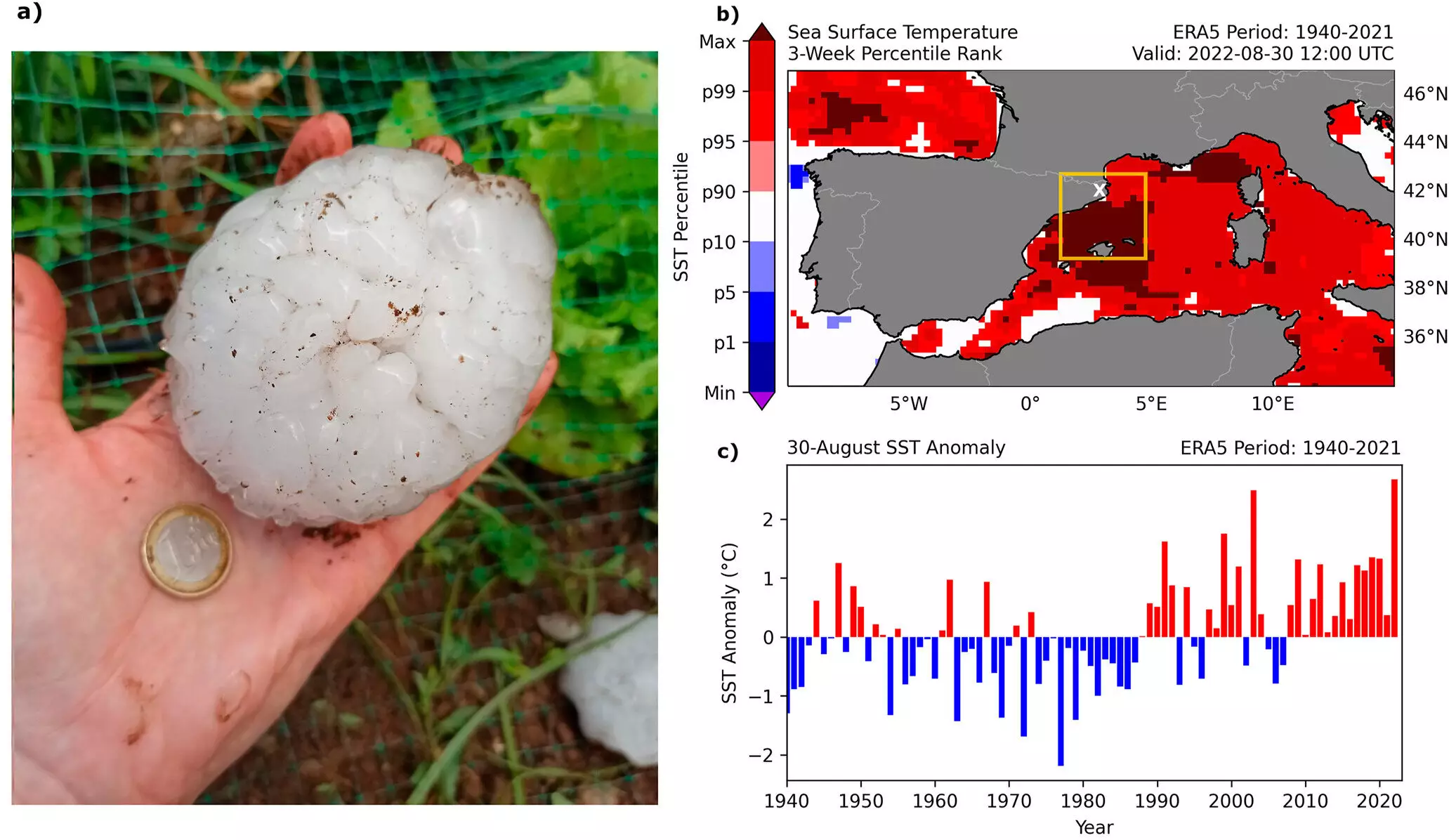
A group of researchers led by Professor Maria Luisa Martin from Universidad de Valladolid, Spain, delved into the underlying causes of this extreme hail event. Their study, published in Geophysical Research Letters, pointed to the significant role played by a record-breaking marine heat wave in exacerbating the hailstorm.
During the summer of 2022, the Iberian Peninsula experienced a notable increase in sea surface temperature, reaching an average of 3.27°C over six weeks. This rise, the highest on record, fueled atmospheric convective energy to unprecedented levels. Coupled with moisture from the warm ocean, this provided ideal conditions for the development of supercells, which in turn led to the formation of large hailstones.
To further understand the correlation between marine heat waves and severe hailstorms, the research team analyzed data from over 280 documented supercell events from 2011 to 2022. The simulations revealed that large hailstorms, exceeding 5cm in diameter, could occur approximately four hours per year. The Maestrazgo region in north-eastern Spain was identified as particularly susceptible to these events due to its role as a focal point for supercell formation.
The study also highlighted the impact of global warming on the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. With increased sea surface temperatures being a direct consequence of climate change, the researchers observed a significant reduction in conditions conducive to hailstorms when the influence of marine heat waves was removed from the models.
Professor Maria Luisa Martin and her team’s research serve as a warning of the potential consequences of continued climate change. The likelihood of marine heat waves and other extreme meteorological events is expected to increase, leading to unforeseen environmental, social, and economic impacts. By understanding the interconnected nature of Earth’s systems, we can better prepare for and mitigate the effects of such events in the future.

Leave a Reply