The recent research findings have shed light on the significance of sustainable chemical transformations in the field of pharmaceutical research. These transformations are crucial for reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of chemical processes. Electrochemistry has emerged as a key player in this arena, offering a more sustainable approach to synthetic chemistry.
The Max Planck Institute of Chemical Energy Conversion (MPI CEC) has been at the forefront of exploring innovative structural motifs in drug discovery. The team of scientists from MPI CEC has demonstrated the power of electrochemistry in driving the development of new synthetic routes for the modern organic chemist’s toolkit. By focusing on the electrochemical conversion of nitro groups, the researchers have unlocked a previously understudied class of N-hydroxy heterocycles with great potential in drug discovery.
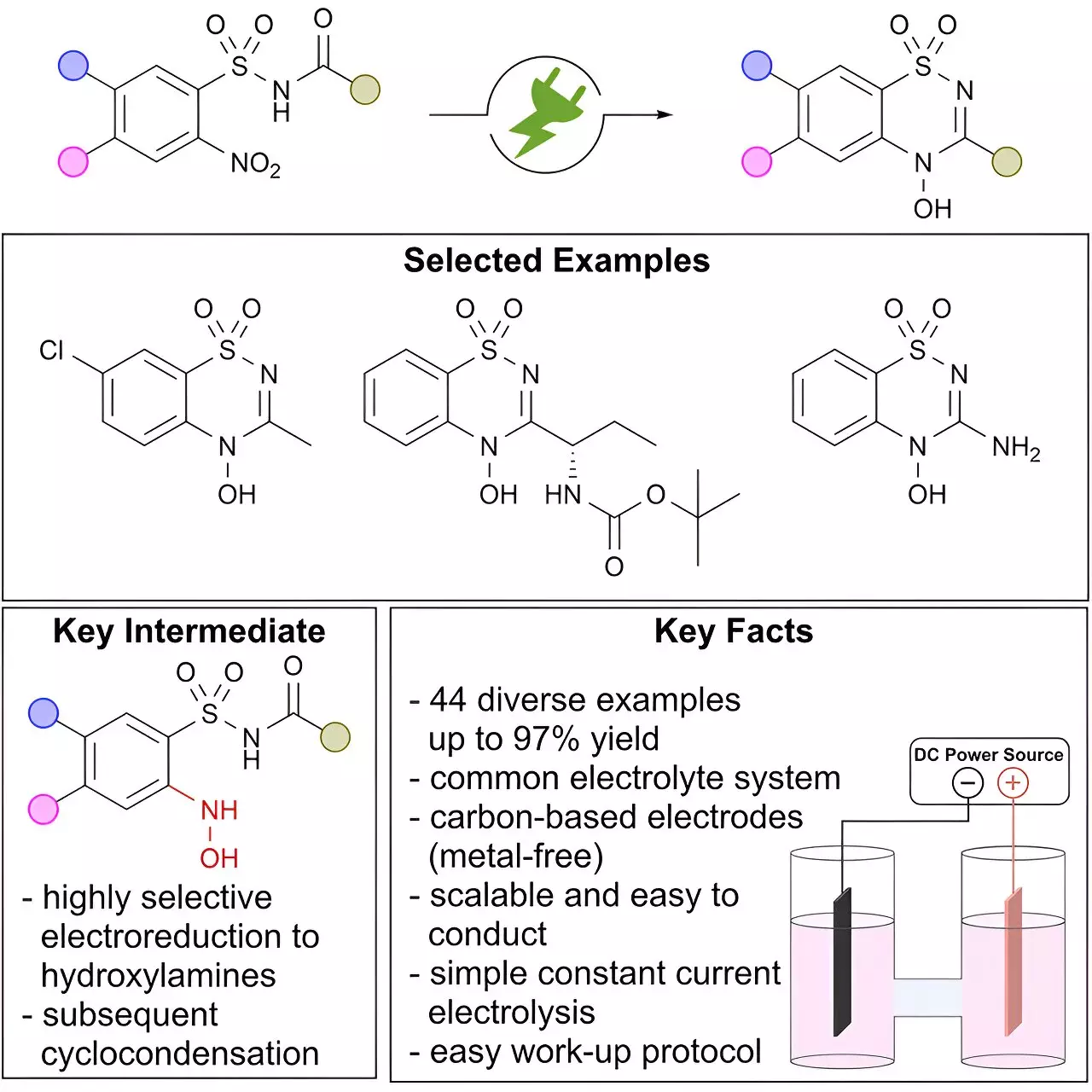
Nitrogen-containing heterocycles, such as benzo[e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxides, are commonly found in blockbuster pharmaceuticals. However, little is known about heterocycles containing an exocyclic N-hydroxy modification. The stability and unique characteristics of the N-O bond make this motif highly intriguing for pharmaceutical research. Electrochemical synthesis has enabled the selective and scalable production of these compounds, which are challenging to access through traditional methods.
Siegfried R. Waldvogel and his team have made a breakthrough in electro-organic synthesis by developing a highly selective and scalable method for producing novel benzo[e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxides modified with a unique N-hydroxy moiety. This method opens up new possibilities for synthesizing compounds that were previously unattainable. The study has expanded the compound library of benzo[e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxides, paving the way for further exploration in pharmaceutical research.
While the biological properties of these novel compounds remain unknown, their investigation could hold the key to improving drug efficiency, understanding metabolism, and exploring new pharmaceutical applications. By leveraging sustainable electro-organic synthesis, researchers have the opportunity to revolutionize drug discovery and development.
The research conducted by the scientists at MPI CEC has highlighted the transformative potential of electro-organic synthesis in pharmaceutical research. By focusing on sustainable chemical transformations and novel structural motifs, researchers are paving the way for the development of more efficient and environmentally-friendly drug synthesis methods. The future of drug discovery looks promising, thanks to innovative approaches like electrochemical synthesis.

Leave a Reply