China is at the forefront of a new era of aviation, driven by significant advancements in unmanned aerial systems (UAS). The nation is on the brink of a transformative shift in low-altitude airspace management, as it grapples with the integration of an increasing number of unmanned aircraft into its national airspace. This evolution presents unique challenges and opportunities for regulation, technology, and industry practices.
The Challenges of UAS Operations
One of the key challenges presented by the digital, networked, and intelligent nature of UAS operations is the need for rapid evolution in traditional aviation regulations and technical systems. With the rise of commercial drones for logistics, environmental monitoring, and potentially passenger transport, China is under pressure to ensure safe, efficient, and integrated airspace usage by a diverse array of new players.
China has historically maintained a complex airspace classification system, dominated by military and commercial aviation. However, since 2010, the nation has initiated reforms for low-altitude airspace management to incorporate general aviation and UAS. The Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC) has taken the lead in establishing low-altitude flight service support systems to facilitate this transition.
Explosive Growth of Drone Manufacturing in China
One of the most notable developments in the airspace management sector is the explosive growth of the UAS industry in China. The nation has emerged as a world leader in drone manufacturing, with drones being extensively used in logistics, agriculture, and environmental sectors. The shift toward unmanned aviation is evident, with UAS flight hours surpassing those of manned aircraft.
The integration of UAS into the national airspace in China is a multifaceted process. It involves the adaptation of UAS traffic management systems, technological tests, and the verification of new operational concepts. China is looking to international practices for guidance in shaping its regulatory framework and operational strategies, including the adoption of advanced traffic management systems to facilitate the safe movement of both manned and unmanned aircraft.
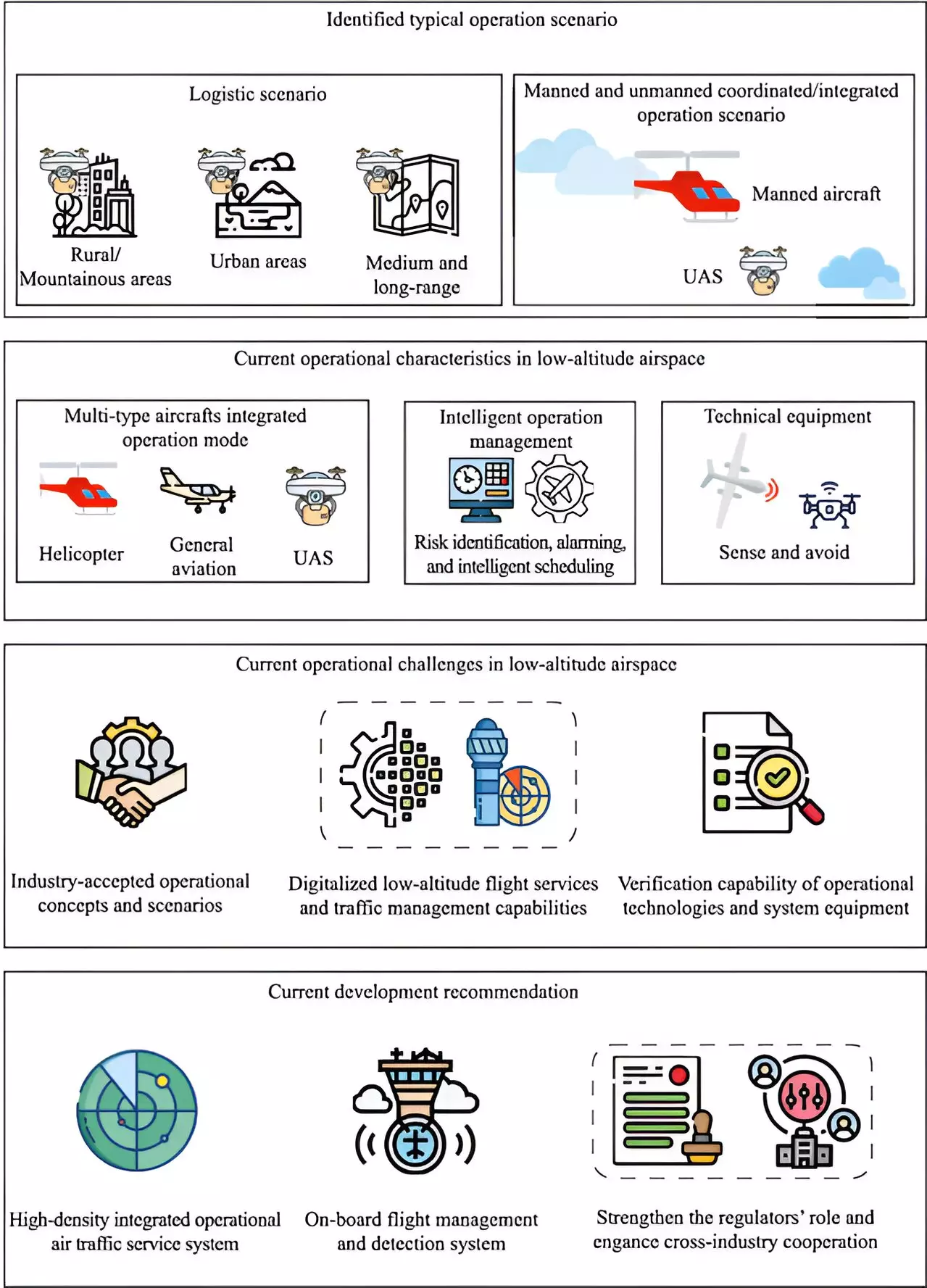
Challenges and Opportunities in UAS Operations
The operational scenarios for UAS in China are diverse, ranging from UAS logistics in urban and rural settings to coordinated operations with manned aircraft. While UAS offer high efficiency and reduced costs in logistics, their rapid integration into populated urban areas comes with significant challenges. Ensuring the safety of manned and unmanned aircraft, integrating advanced traffic management technologies, and developing operational standards are critical considerations.
The Future of UAS in China
Looking ahead, China is poised to significantly expand the role of UAS, with broader applications in passenger transport and increased use in international logistics. Continuous advancements in technology and regulatory frameworks will be necessary to ensure safety and efficiency in this evolving landscape. As China refines its approach to low-altitude airspace management, the global aviation industry is closely monitoring its progress. The country’s journey toward fully integrated UAS operations not only showcases its technological prowess but also its potential to set international standards in unmanned aviation. Through ongoing research, development, and regulatory adjustments, China is laying the foundation for a future where drones play a central role in the national airspace ecosystem.

Leave a Reply