Modern building design methods have traditionally focused on enhancing the connectivity between various structural components to ensure the redistribution of loads in case of component failure. However, while this approach is effective in mitigating small failures, it can pose a significant risk of progressive collapse following large initial failures. Recent tragic incidents, such as the collapse of Champlain Towers, a building in Peñíscola, and a structure in the Iranian city of Abadan, underscore the urgent need for alternative design solutions to prevent catastrophic building collapses.
A groundbreaking approach proposed by the ICITECH-UPV team offers a novel design method to address the limitations of traditional building design. This innovative technique, as detailed in a publication in the journal Nature, introduces the concept of structural fuses to isolate damaged sections of a building, thereby preventing the spread of failures and safeguarding the overall structure. Co-author Jose M. Adam emphasizes the significance of this new approach in enhancing building resilience and minimizing the risk of total collapse.
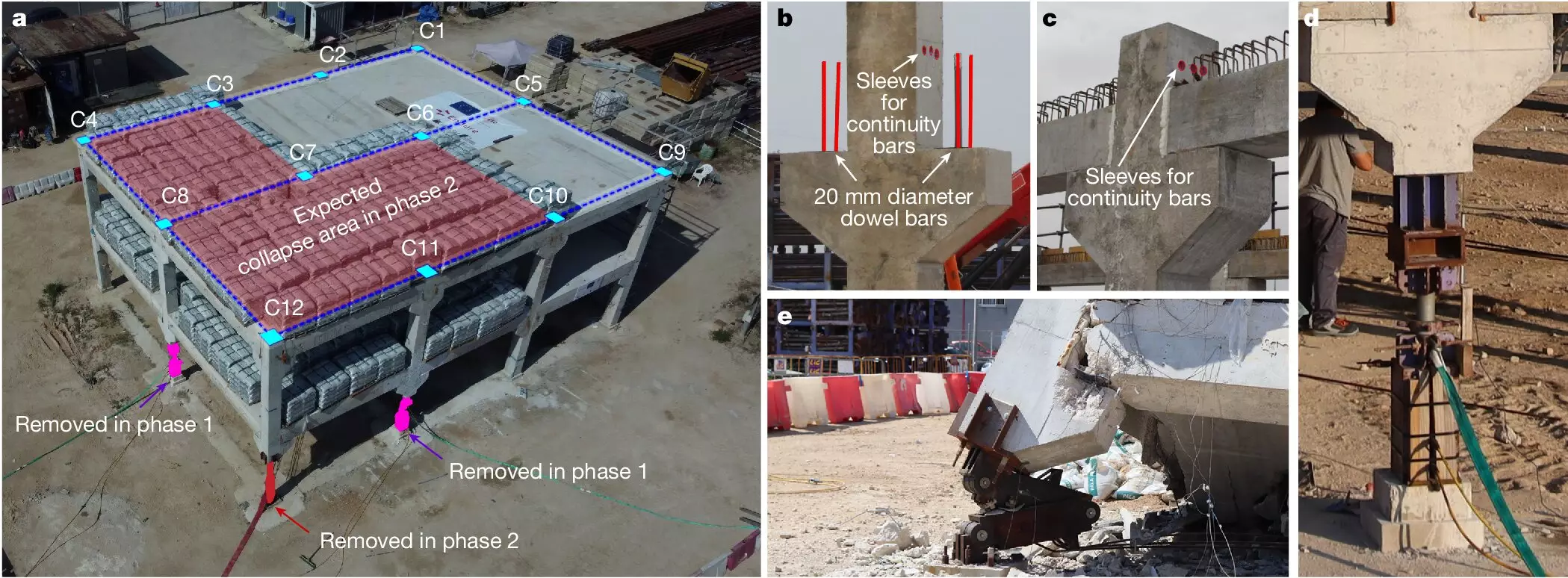
The effectiveness of the fuse-based segmentation method has been validated through a real-scale building test, marking a significant milestone in building safety research. This test represents the first successful demonstration of a solution to halt collapse propagation after significant structural failures. Moreover, the implementation of this design method in new constructions is anticipated to have minimal impact on construction costs, utilizing standard building materials and techniques. Researchers, including Nirvan Makoond, Andri Setiawan, and Manuel Buitrago, stress the adaptability of this method to various construction types, offering a versatile solution for enhancing building safety.
The ongoing development of this innovative design method within the framework of the Endure project signifies a crucial advancement in building safety standards. Continued research aims to extend the application of fuse-based segmentation to diverse building materials, including in-situ concrete and steel structures. The successful validation of this approach in a full-scale building test highlights the potential for widespread adoption in future construction projects. With all research conducted at the UPV by dedicated scholars, the fuse-based segmentation method presents a promising solution to prevent catastrophic building failures and preserve human lives.
The introduction of fuse-based segmentation in building design represents a paradigm shift in the field of structural engineering. By isolating damaged sections and preventing collapse propagation, this innovative method offers a robust solution to enhance building resilience and safety. As ongoing research continues to refine and expand the application of this approach, the future of construction holds the promise of more secure and reliable structures, ultimately saving lives and safeguarding against economic losses. The fuse-based segmentation method stands as a testament to the crucial role of innovation in addressing pressing challenges in the built environment.

Leave a Reply