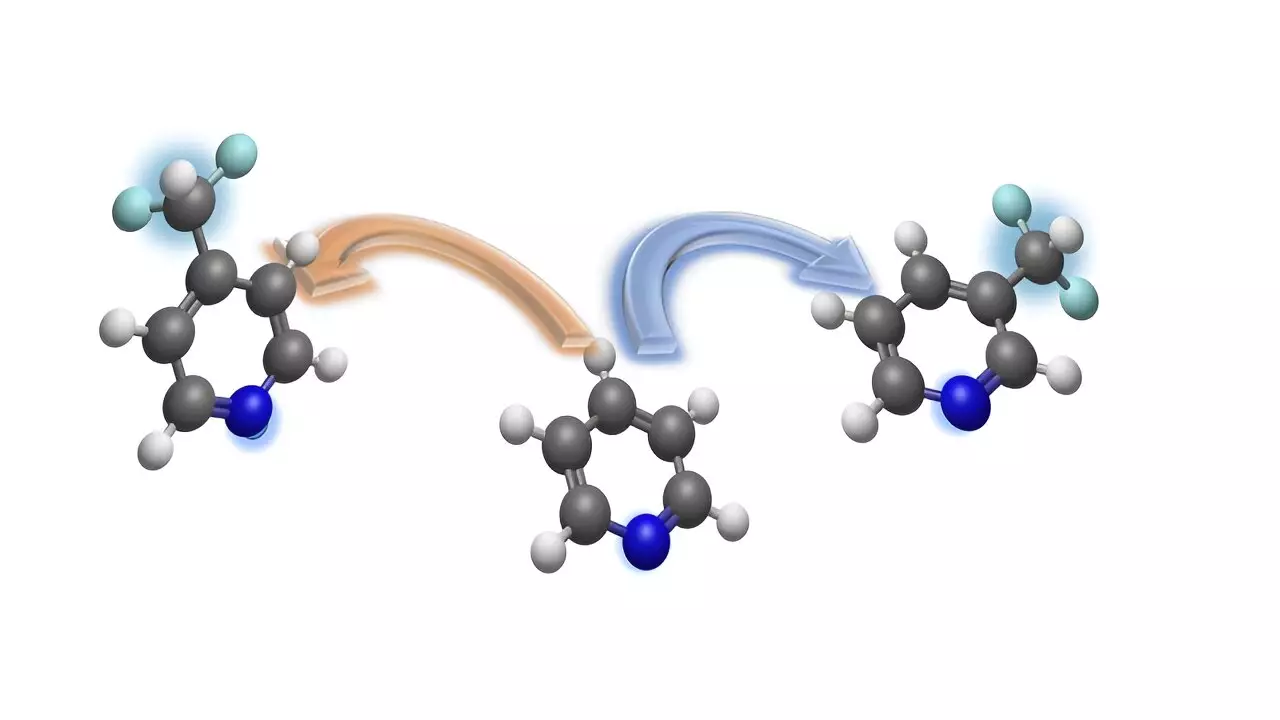
In a recent study conducted by a team of chemists at the University of Münster, a new synthesis method has been developed for the site-selective integration of the biologically relevant difluoromethyl group into pyridines. This breakthrough has significant implications for drug research, as the difluoromethyl group plays a crucial role in determining the properties of bioactive molecules.
Importance of Difluoromethyl Group in Drug Research
The difluoromethyl group, consisting of carbon, two fluorine atoms, and a hydrogen atom, is particularly interesting for drug research due to its impact on the efficacy of bioactive molecules. By incorporating difluoromethyl groups into pyridine derivatives, chemists can obtain difluoromethylated ring structures that hold promise as potential candidates for new drugs and agrochemicals.
Led by Prof Dr. Armido Studer, the team of researchers at the University of Münster has presented a new strategy for the precise introduction of the difluoromethyl group into pyridines at specific sites. This method, outlined in the journal Nature Communications, offers a solution to the challenge of regioselective difluoromethylation of pyridines.
Advantages of the Method
The innovative method allows for the introduction of the difluoromethyl group at either the meta-position or para-position of the pyridine ring, providing flexibility and control in the synthesis process. This approach is particularly valuable for accessing the meta-position, which was previously difficult to target in complex compounds.
Pyridine derivatives are essential building blocks in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industry, making the site-selective integration of difluoromethyl groups a significant advancement in drug design. The use of temporary dearomatization strategies enables the conversion of pyridines into chemically functionalized compounds, simplifying the synthesis process for drug development.
Overall, the development of a method for the site-selective integration of difluoromethyl groups into pyridines represents a significant advancement in drug research. The practicality and cost-effectiveness of this approach make it a valuable tool for chemists in the field of drug design, offering new possibilities for the synthesis of bioactive molecules.

Leave a Reply