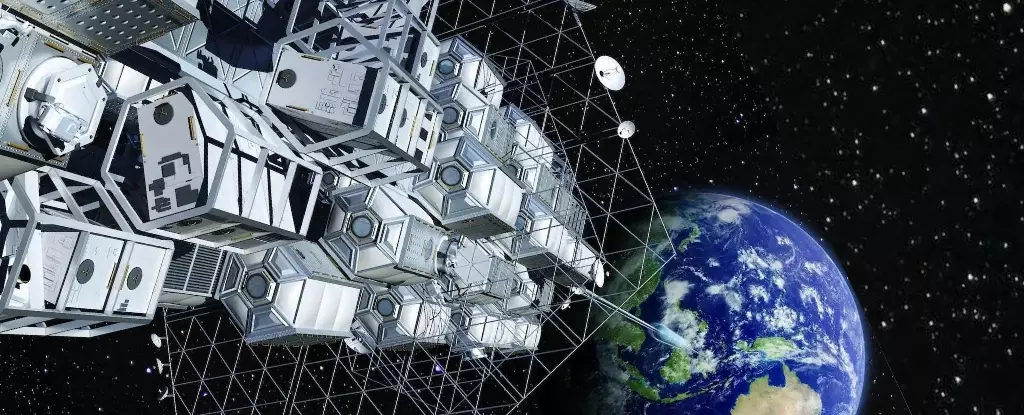
The concept of a space elevator holds the promise of transforming space travel as we know it. By envisioning a long tether connecting Earth to space, the potential exists to drastically reduce the time and cost associated with launching objects into orbit and beyond. Estimates suggest that a space elevator could cut the travel time to Mars from six to eight months down to as little as 40 days, opening up new frontiers in space exploration. Additionally, the elimination of the need for traditional rockets and fuel could revolutionize the transportation of goods and humans into space.
While the concept of a space elevator is captivating, the engineering challenges associated with constructing such a structure are immense. The idea of creating a tether strong enough to withstand the tension required to reach space presents significant hurdles. Traditional materials like steel would be insufficient due to the amount required, leading researchers to explore alternatives such as carbon nanotubes. While carbon nanotubes offer strength and lightness, the current limitations in their length pose a major obstacle in realizing the full potential of a space elevator.
The development of a space elevator relies heavily on technological innovation and collaboration across various industries. Researchers and engineers are continuously exploring new materials and methods to overcome the current limitations and make the concept a reality. Partnerships between companies, governments, and scientific communities are essential to pool resources and expertise in addressing the multifaceted challenges associated with building a space elevator.
The financial implications of constructing a space elevator are substantial, with estimates reaching up to $100 billion for the project. Raising funds and securing investments are crucial aspects of moving the initiative forward. However, proponents of a space elevator view it as a new kind of public works project that could benefit humankind on a global scale. The potential to significantly reduce the cost of transporting goods into space could have far-reaching implications for industries and scientific research.
Despite the ambitious vision of building a space elevator, numerous obstacles remain to be addressed. The challenges of material strength, weather conditions, and overall feasibility present formidable barriers to the realization of this concept. However, proponents like the Obayashi Corporation remain optimistic about the future potential of a space elevator. While the timeline for construction and operation by 2050 may be ambitious, the pursuit of this groundbreaking project continues to inspire innovation and collaboration in the pursuit of new frontiers in space travel.

Leave a Reply