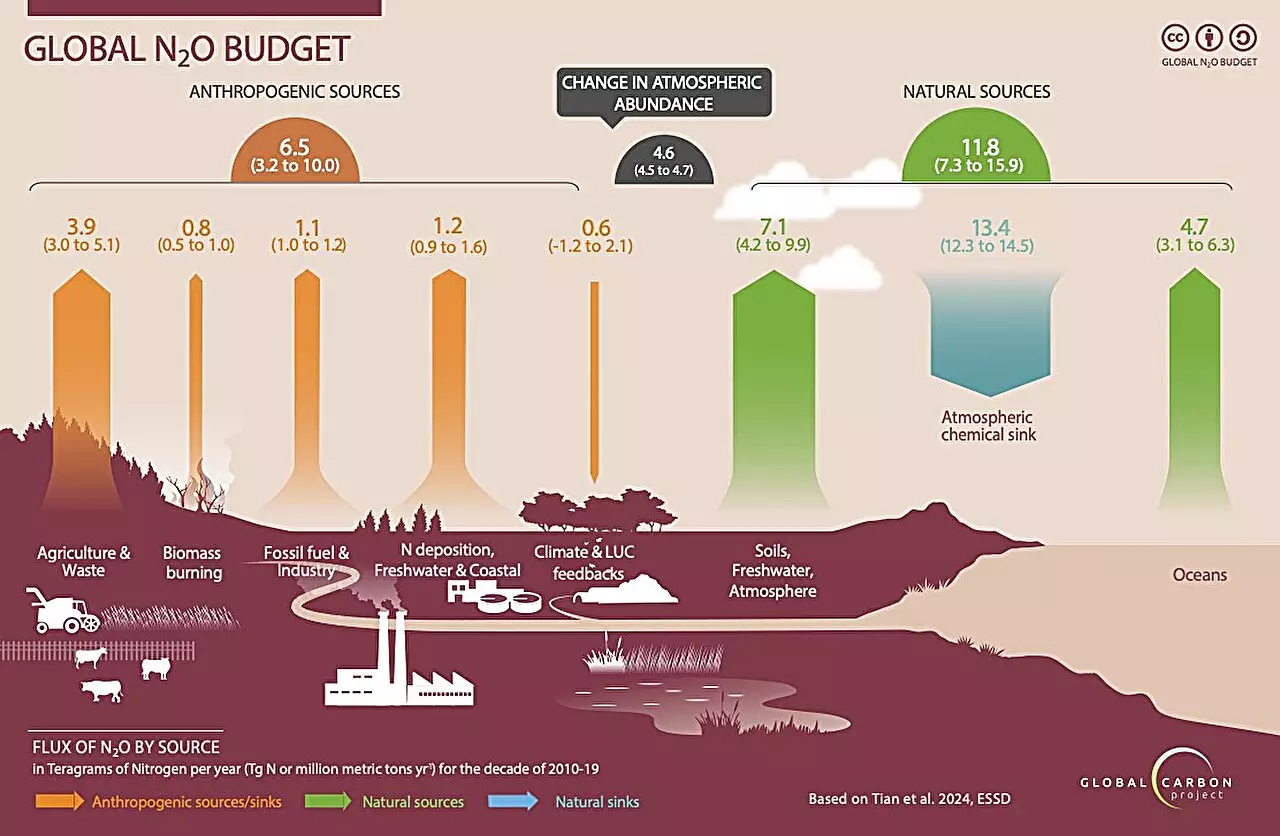
The emissions of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, have continued to rise unchecked from 1980 to 2020. A recent report by the Global Carbon Project reveals that over 10 million metric tons of nitrous oxide were released into the atmosphere in 2020, primarily due to farming practices. The use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands has been identified as the main contributors to these emissions.
Agricultural activities accounted for 74% of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s, highlighting the significant role that farming plays in exacerbating climate change. Nitrous oxide emissions have increased by 67% since 1980, reaching 8 million metric tons in 2020. These emissions are a serious concern as nitrous oxide is approximately 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of global warming potential.
Global Trends and Consequences
The concentration of atmospheric nitrous oxide has reached alarming levels, with a 25% increase over pre-industrial levels. This trend far surpasses previous predictions made by experts. The top 10 countries contributing to nitrous oxide emissions include China, India, the United States, Brazil, and Russia. Despite some regions showing success in reducing emissions, overall levels continue to rise globally.
It is crucial for countries to take immediate action to curb nitrous oxide emissions. The lead author of the report, Hanqin Tian, stresses the need for reducing nitrous oxide emissions to limit global temperature rise in line with the Paris Agreement. However, there are currently no technologies available to remove nitrous oxide from the atmosphere, making emission reductions imperative.
Recommendations for Mitigation
One of the key recommendations to reduce nitrous oxide emissions is to improve agricultural practices. Limiting the use of nitrogen fertilizers and managing animal waste more efficiently can significantly decrease emissions. Monitoring and assessing high-emission regions and activities are essential for effective mitigation efforts.
The continuous rise in agricultural emissions of nitrous oxide poses a significant threat to the environment and contributes to the acceleration of global warming. It is crucial for governments, industries, and individuals to work together to reduce nitrous oxide emissions and adopt sustainable practices to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Failure to address this issue could have catastrophic consequences for the planet’s future.

Leave a Reply