In recent years, the urgent demand for sustainable energy sources has prompted an inevitable evolution in battery technology, particularly as electric vehicles (EVs) seek to dominate the automotive market. Traditional lithium-ion batteries, dominating the ecosystem, rely heavily on nickel and cobalt – materials that are becoming increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impact and scarcity. As the landscape shifts toward eco-friendly alternatives, manganese—a more abundant element—emerges as a promising candidate. The latest research unveiled in ACS Central Science illuminates this path forward, revealing the innovative design of nanostructured lithium manganese dioxide (LiMnO2) as a viable, sustainable option for battery production.
The Chemistry Behind LiMnO2 and Its Structural Advantages
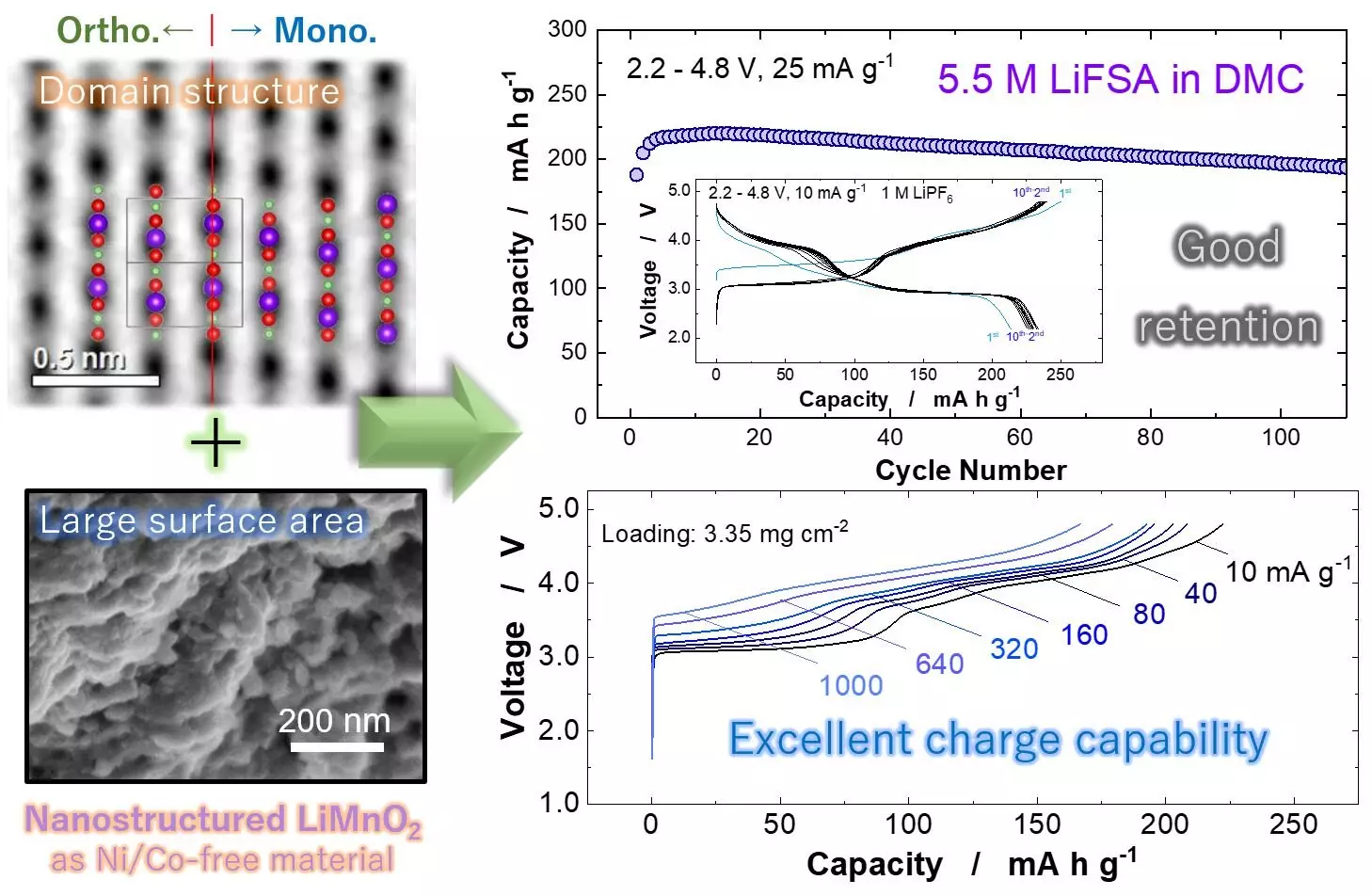
At the heart of this exciting new development is the crystalline arrangement of LiMnO2. Researchers have systematically explored various polymorphs of lithium manganese oxide, unveiling unique properties associated with a monoclinic symmetry. This configuration aids in facilitating critical structural transitions, which significantly enhance performance capabilities, a prospect long elusive for previous iterations of manganese-based materials. Naoaki Yabuuchi, one of the leading researchers, highlighted this promising direction through the synthesis of nanostructured LiMnO2 that maintains high surface area and intrinsic stability—key traits for high-demand applications in electric vehicles.
The monoclinic structural attribute provides the needed flexibility in performance, allowing the material to transition without compromising efficiency. This noteworthy feature resolves the limitations seen with earlier LiMnO2 forms that suffered due to suboptimal crystallinity. The finding punctuates the importance of material science in the evolution of energy storage solutions, suggesting that the future of battery efficiency lies in our ability to manipulate molecular structures to maximize their performance.
Performance Metrics That Outshine Traditional Options
One of the standout features of the newly synthesized nanostructured LiMnO2 lies in its impressive energy density of 820 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh kg-1). This makes it a worthy competitor against nickel-based materials, which typically deliver around 750 Wh kg-1. The leap in performance is crucial, especially when considering the escalating demands for fast-charging capabilities in EVs. As consumers express a growing need for quick recharge times to parallel the convenience provided by fossil fuel-powered vehicles, the development of a battery that meets these needs becomes paramount.
Additionally, the absence of voltage decay—commonly associated with manganese-based materials—underscores the significance of this innovation. The perseverance of battery performance over time is crucial for consumer trust and product longevity. Delivering consistent performance without the gradual diminishing of efficacy could revolutionize how we perceive battery life and sustainability in EV technology.
Challenges Ahead: Addressing Manganese Dissolution
Despite the promising advancements, the journey does not come without hurdles. One of the ongoing challenges is the dissolution of manganese, which poses a risk of reducing battery life. However, the research suggests pragmatic solutions—such as utilizing a highly concentrated electrolyte solution and applying a lithium phosphate coating—that can significantly alleviate this issue. This strategic approach not only preserves the structural integrity of the battery but also enhances its longevity, thus answering crucial questions about durability and reliability.
The resilience of the battery framework against environmental factors signifies an essential step towards achieving commercial viability. As researchers grapple with these limitations, the potential to transform the automotive industry into a greener and more sustainable future remains tantalizingly close.
Commercialization: The Road Ahead for Nanostructured LiMnO2
As we pivot towards a future dominated by electric vehicles, the commercial prospects for LiMnO2 batteries seem bright. With growing recognition in industries focused on luxury EVs, the chance for large-scale adoption appears promising. Concerns over ethical sourcing, environmental degradation, and costs are paving the way for materials that not only address current limitations but circumvents them altogether through innovative scientific approaches.
Researchers are optimistic that the advancements in LiMnO2 technology can lead to a paradigm shift in manufacturing practices, integrating sustainability at every level, from production to end use. As energy demands escalate globally, the call for efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternatives has never been louder, propelling us toward a redefining moment in how we power our lives. The future is undeniably in motion, charging ahead with the potent synergy of science and sustainability.

Leave a Reply