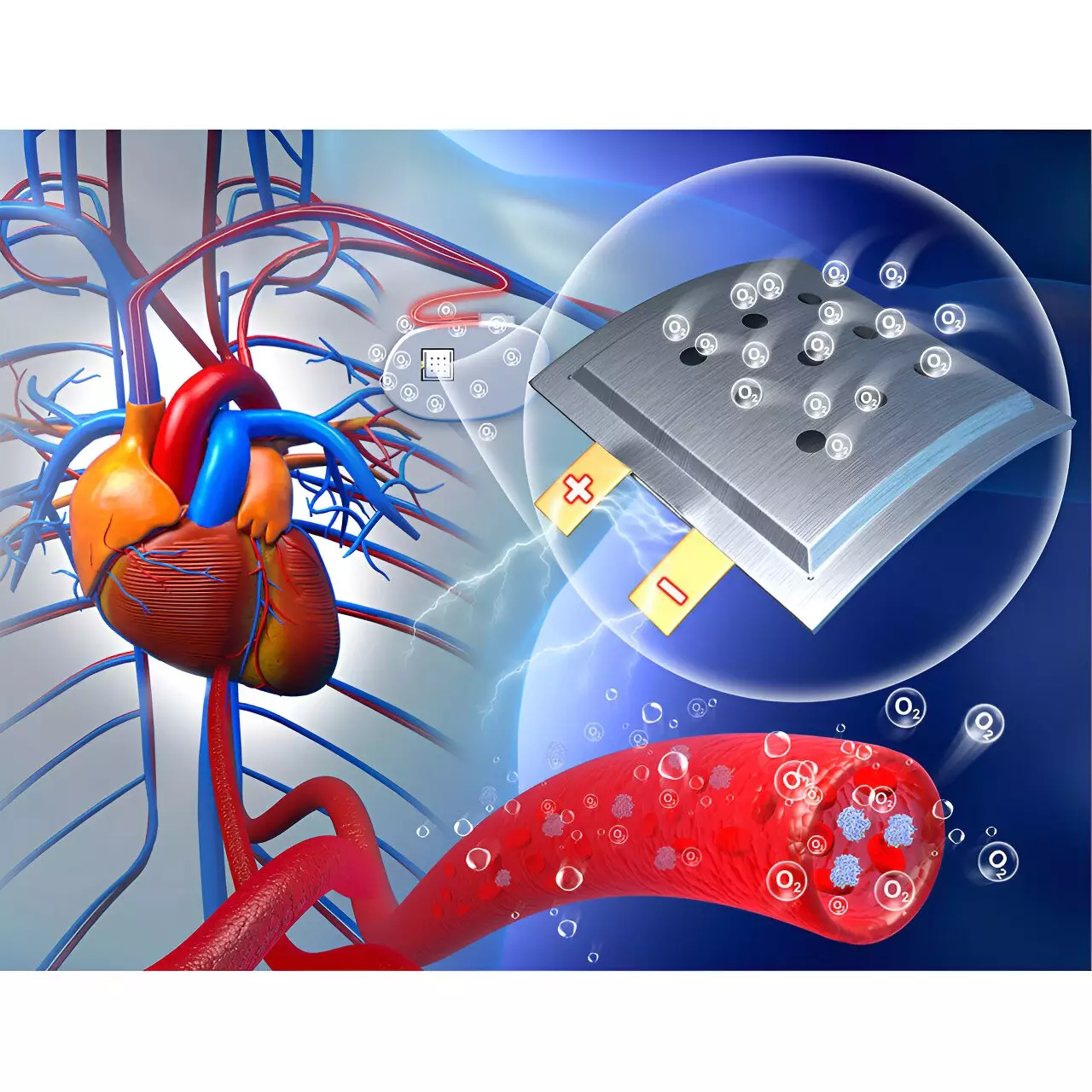
Implantable medical devices have long relied on traditional batteries to function, but these batteries eventually run low and require invasive surgeries for replacement. However, researchers in China have developed a revolutionary implantable battery that runs on oxygen within the body, offering a potential solution to this issue.
The key innovation behind this new implantable battery is the use of electrodes made from a sodium-based alloy and nanoporous gold. These materials undergo chemical reactions with oxygen in the body to produce electricity, providing a continuous and stable source of power. The battery is also encased in a porous polymer film to ensure safety and flexibility.
In a study published in the journal Chem, researchers implanted the battery under the skin of rats and monitored its performance. They found that the battery could produce stable voltages between 1.3 V and 1.4 V, with a maximum power density of 2.6 µW/cm2. While this output may not be sufficient to power medical devices, it demonstrates the feasibility of harnessing oxygen in the body for energy.
Biocompatibility and Healing
One of the notable findings from the study was the biocompatibility of the battery. The rats showed no signs of inflammation, and the byproducts of the battery’s chemical reactions were easily metabolized by the body. Moreover, the rats experienced rapid tissue regeneration around the battery site, with blood vessels regrowing and aiding in stable electricity output.
Future Directions
Moving forward, the research team plans to enhance the battery’s energy delivery by exploring more efficient electrode materials and optimizing the battery’s structure and design. They also aim to scale up production and reduce costs by selecting cost-effective materials. Additionally, the battery’s potential applications extend beyond medical devices, as it could potentially be used to starve cancer cells by consuming oxygen or to generate heat for cancer cell destruction.
The development of an implantable battery that runs on oxygen represents a significant advancement in the field of medical technology. This innovative approach not only provides a sustainable power source for medical devices but also has the potential to impact other areas of healthcare, such as cancer treatment. With further research and development, this technology could revolutionize the way we power and monitor implantable medical devices in the future.

Leave a Reply