Large language models (LLMs) have been a topic of fascination due to their ability to understand written prompts and generate responses that closely resemble human language. The GPT-4 model, which powers platforms like ChatGPT, has astounded users with its conversational capabilities in various languages. Researchers at UC San Diego recently delved into the question of whether these models can truly mimic human-like intelligence by conducting a Turing test.
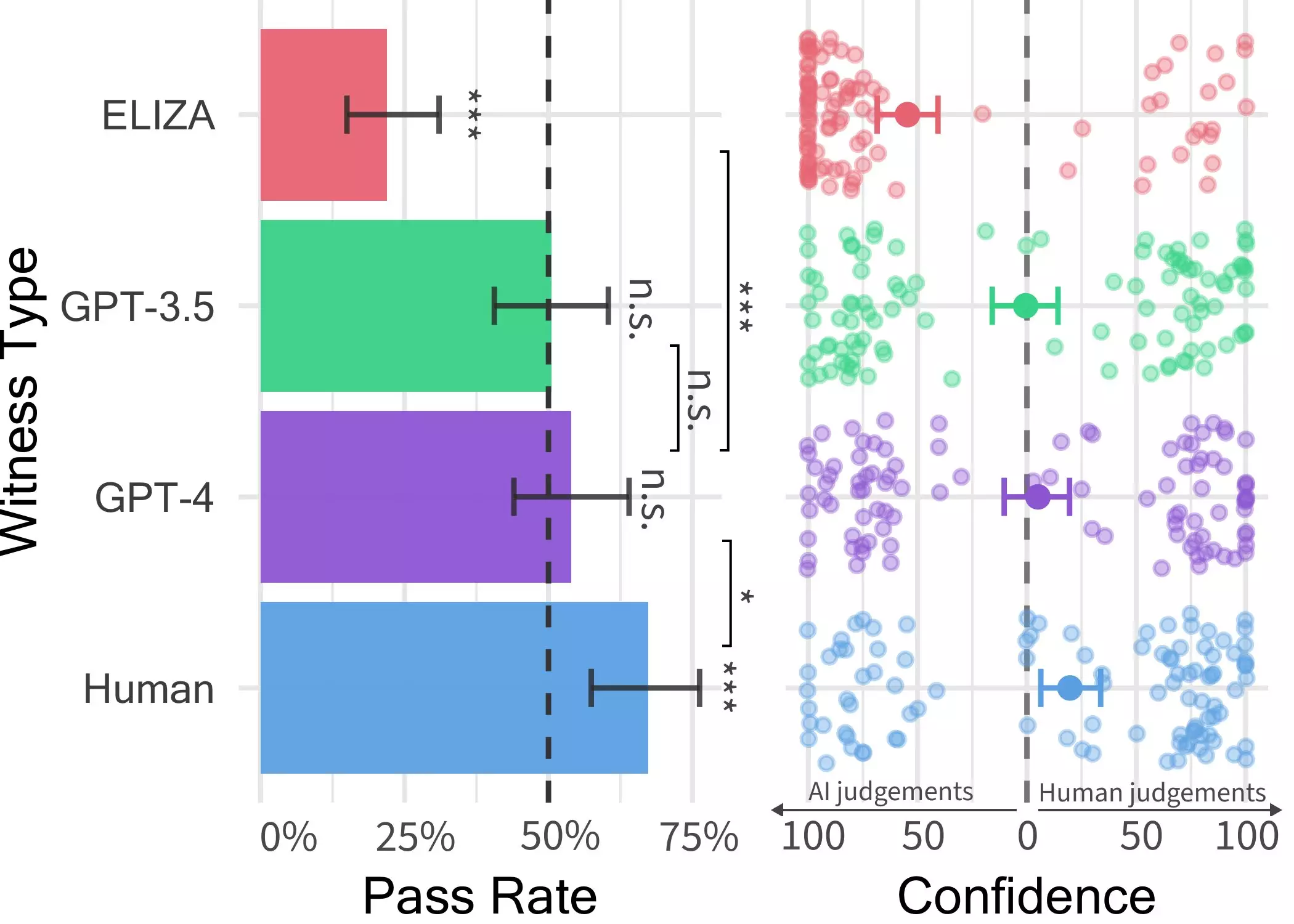
The study, outlined in a paper pre-published on the arXiv server, aimed to assess how well the GPT-4 model could pass as human in a 2-person conversation setting. The initial experiment indicated that the model could successfully masquerade as human in roughly 50% of interactions. However, recognizing the need to control for variables that could impact the outcomes, the researchers conducted a subsequent experiment to obtain more robust results.
Jones and his colleagues developed a two-player game where human participants interacted with either another human or an AI agent (GPT-4, GPT 3.5, or ELIZA). The interrogator engaged in a conversation with a “witness” and had to determine whether the witness was human or machine based on their responses. Interestingly, participants struggled to differentiate GPT-4 from humans, highlighting the model’s ability to simulate human-like conversations effectively.
Implications and Future Research
The implications of these findings are profound, suggesting that AI systems, particularly advanced LLMs like GPT-4, could blur the lines between human and machine interactions in online communication. This phenomenon may lead to increased skepticism and uncertainty among individuals engaging in digital conversations. Jones and Bergen plan to expand their research by exploring novel methods, such as a three-person version of the game, to gain deeper insights into the discernibility of humans and LLMs.
Overall, the study sheds light on the remarkable capabilities of LLMs and raises important questions about the future of human-AI interactions. The rapid advancements in natural language processing continue to challenge our perceptions of artificial intelligence and its potential applications in various domains. As we progress further into the era of AI-driven communication, it becomes imperative to critically evaluate the implications of these technologies on society and human relationships.

Leave a Reply