As the world collectively takes steps toward diminishing its reliance on fossil fuels, the search for alternative energy carriers is more critical than ever. One of the leading candidates in this quest is hydrogen, heralded for its clean combustion properties and environmental benefits. Yet, the pathway to a hydrogen economy is fraught with challenges due to the inherent difficulties associated with hydrogen storage and transportation. Storing hydrogen gas safely requires exceedingly high pressures or frigid temperatures, which not only complicate logistics but also demand significant energy resources. While hydrogen boasts remarkable potential, inherent setbacks necessitate exploration into alternatives that can bridge the gap toward a clean and sustainable energy future.
A Paradigm Shift with Ammonia
Emerging from the shadows of hydrogen is ammonia (NH3), a compound that possesses unique advantages over its gaseous counterpart. A collaborative research team led by Associate Professor Kosuke Ono from the Tokyo Institute of Technology and Tokyo University of Science has pioneered an innovative solution for ammonia storage, creating a novel material known as 1a. This compound can adsorb and desorb ammonia at high densities, effectively circumventing the significant limitations faced by hydrogen storage technologies. With ammonia requiring less rigorous storage conditions, it presents itself as a much more versatile vehicle for energy transfer, with existing infrastructure readily adapted to accommodate its transport.
Unlike hydrogen, ammonia combustion yields nitrogen and water—both innocuous byproducts—making it a carbon-free energy carrier. This distinct environmental advantage aligns with growing global demands for cleaner energy solutions. The work by Ono and his team demonstrates that harnessing ammonia could be pivotal in the transition toward sustainable energy systems while ensuring energy security.
The Chemical Innovation Behind 1a
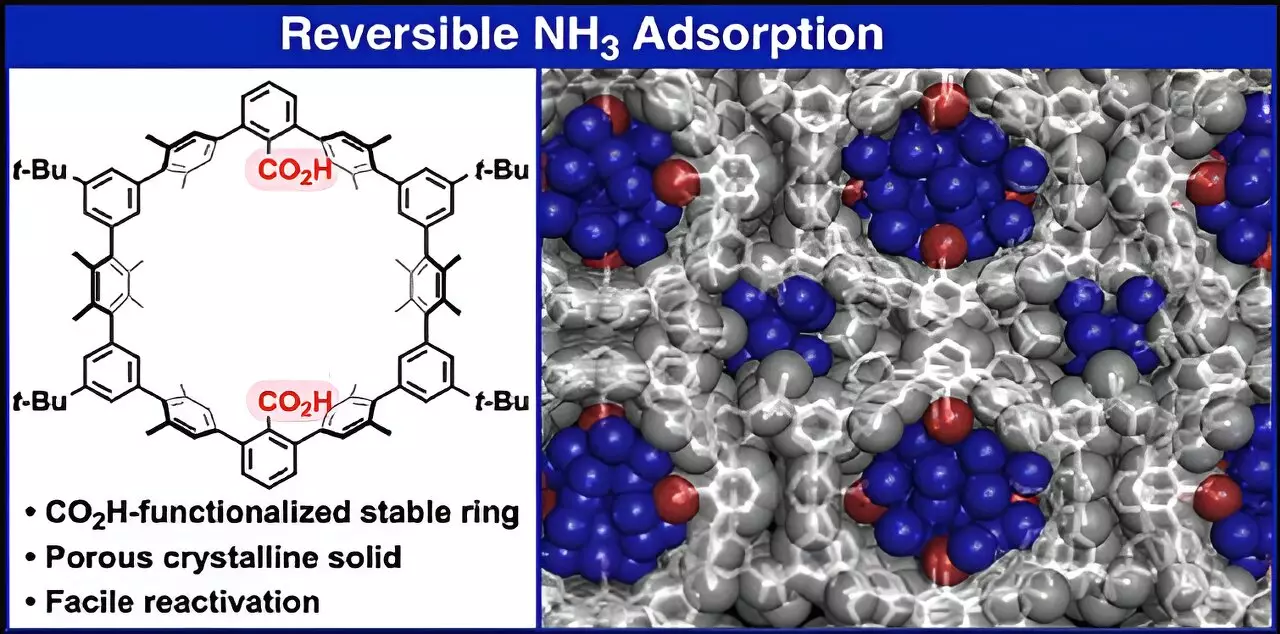
The breakthrough lies in the engineering of the 1a crystalline solid, composed of cyclic oligophenylenes with CO2H groups integrated into their structure. This configuration is not merely sophisticated, but it lays the groundwork for facilitating effective NH3 adsorption. When arranged into a porous solid structure, the hydrocarbon chains create parallel nanochannels, enhancing the material’s capacity to absorb and store ammonia at remarkably high densities—comparable to liquid ammonia. This innovative approach not only solves the storage conundrum but also extends the lifecycle and usability of the material.
A critical advantage of 1a is its ability to efficiently release stored ammonia by simply lowering the surrounding pressure. This method of desorption alleviates issues commonly associated with traditional NH3 storage materials, where residues can hinder performance. This technological leap not only streamlines the process but also guarantees that 1a is viable for repeated applications, opening the door to large-scale possibilities.
Implications for a Hydrogen Economy
The implications of this research extend beyond the confines of a laboratory. The introduction of 1a represents a transformative step in ammonia’s role as a sustainable energy carrier, potentially reshaping industries reliant on fossil fuels. The possibility of utilizing ammonia on a grand scale can minimize greenhouse gas emissions while providing a stable energy source. Furthermore, the ease of production and preparation of 1a underlines its cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for various industries.
The inventiveness surrounding ammonia does not stop here; with continued exploration, modifying the chemical structure of 1a may allow it to adsorb other gases that are generally challenging to handle, such as hydrogen chloride or chlorine gas. This flexibility presents an exciting avenue for future research and development, expanding the horizons of gas storage materials and opening doors to innovative applications.
A Call to Action
With global energy demand ever-increasing, and climate challenges looming large, the understanding and development of sustainable energy alternatives like ammonia must accelerate. The research led by Ono is more than just an academic achievement; it is a clarion call to industry, governments, and researchers to embrace ammonia and other innovative technologies that could redefine the energy landscape. This shift could create robust frameworks for sustainable practices, urging us to not only imagine but realize a future with cleaner energy and a healthier planet. The time has come to pivot our strategies and invest in dynamic energy solutions that align with our ecological goals.

Leave a Reply