In a landmark advancement for renewable energy, a team from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has unveiled a groundbreaking method to improve the durability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). This innovative research, encapsulated in the paper “Chiral-Structured Heterointerfaces Enable Durable Perovskite Solar Cells” published in the journal Science, signifies a vital step towards harnessing solar energy more effectively and economically. As the quest for sustainable energy sources intensifies, such breakthroughs not only enhance the scientific landscape of solar technology but also provide a glimpse into a cleaner, greener future for electricity generation.
Understanding the Promise of Perovskite Solar Cells
At the core of this research is the perovskite solar cell, which utilizes materials characterized by a perovskite crystal structure. What makes PSCs particularly appealing is their cost-efficiency and simplified manufacturing processes compared with traditional silicon-based solar cells. Silicon solar cells generally rely on expensive and energy-intensive fabrication techniques, often involving high-temperature processes and vacuum environments. In contrast, perovskites can be deposited in thin layers using various inexpensive printing technologies, making them a compelling alternative in the transition towards renewable energy.
Despite their rapid progress in efficiency—PSCs have seen dramatic performance gains in recent years—their commercial viability has faced critical challenges. One persistent issue has been the stability of these cells when exposed to real-world conditions. Environmental factors can significantly affect their performance, leading to a pressing need for solutions that bolster reliability.
Addressing Durability Through Innovation
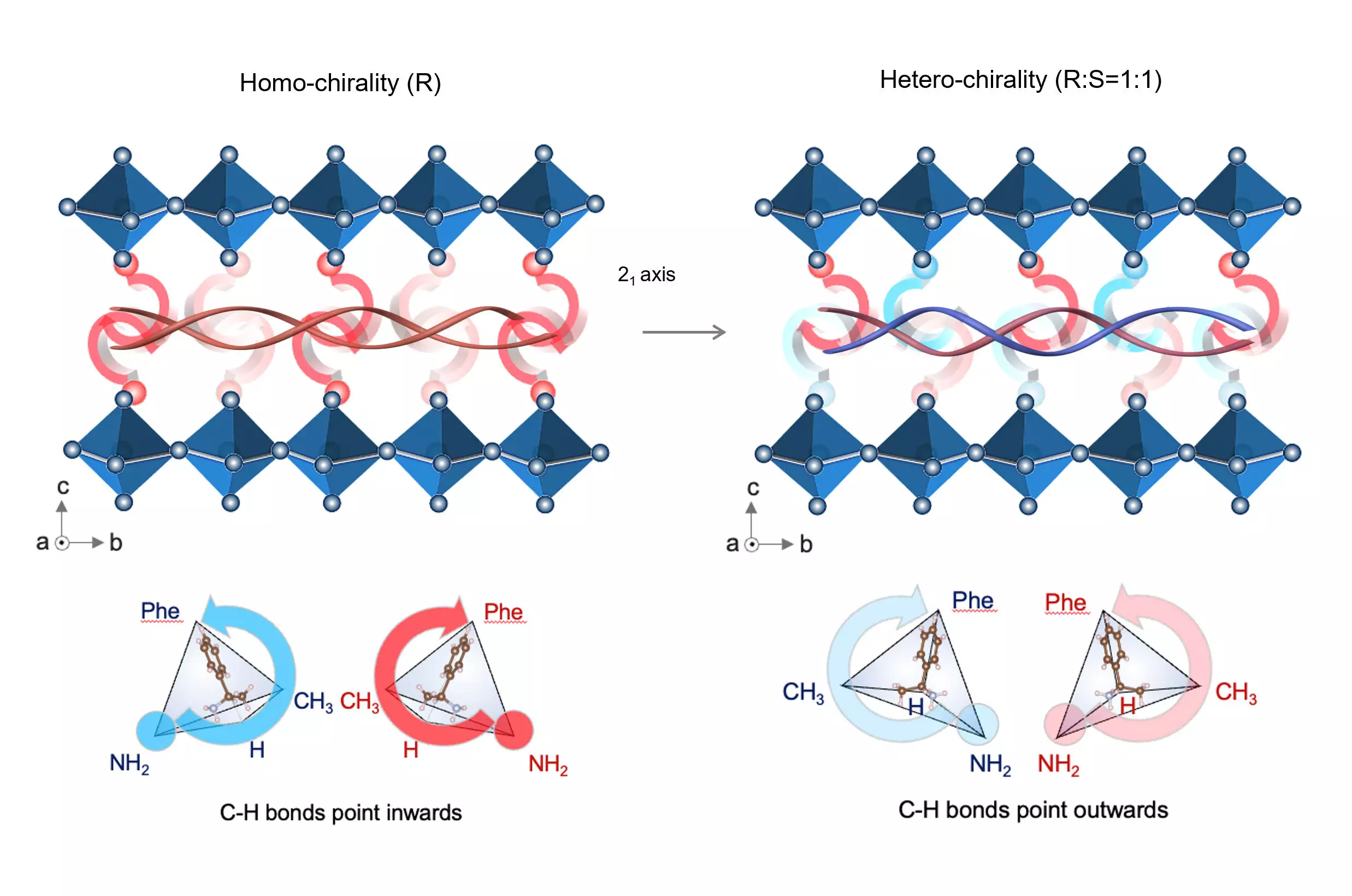
The crux of the HKUST team’s solution lies in addressing the insufficient adhesion between the layers of PSCs. Poor interfacial stability has historically plagued the performance of perovskite devices. By drawing inspiration from natural chiral materials, which possess an extraordinary mechanical strength derived from the helical arrangement of their molecular structures, the researchers devised a unique chiral-structured interface that significantly enhances interfacial reliability.
Prof. Zhou Yuanyuan and Dr. Duan Tianwei led the charge in this research. Their innovative approach involved introducing chiral interlayers consisting of R-/S-methylbenzyl-ammonium between the essential layers of the solar cells. The resulting elastic heterointerface not only improves mechanical strength but also adapts effectively to fluctuating operational conditions. The findings from rigorous testing are striking; the encapsulated cells maintained 92% of their power conversion efficiency even after 200 cycles at extreme temperatures, complying with stringent International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards.
The Significance of Chiral Structures
The introduction of chiral structures in solar technology represents a pivotal moment for energy research. Chiral materials, known for their intricate physical properties and resilience, resemble mechanical springs due to their unique helical organization. This quality allows for greater flexibility and durability, making perovskite solar cells not only more reliable but also capable of performing across a broad range of environmental conditions.
Dr. Duan articulates the importance of these developments, noting, “Incorporating a chiral-structured interlayer at the crucial device interface makes the perovskite solar cell more mechanically durable and adaptable under various operational states.” This remarkable insight underscores the potential of marrying biological principles with engineering to foster advancements in renewable energy technologies.
A Bright Future for Solar Power
As we stand at this critical juncture, the implications of this research extend far beyond the laboratory. Prof. Zhou enthusiastically points out the transformative impact this could have on energy markets globally, stating, “If we could ultimately overcome the reliability issue, billions of energy markets will be seen.” The promise of enhanced durability and efficiency positions PSCs favorably against traditional energy sources, putting us on a path towards widespread adoption of solar technology.
This breakthrough signals not only a scientific triumph but also a crucial milestone in addressing global energy challenges. By boosting the reliability of perovskite solar cells, we pave the way for an era where sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective solar energy becomes a norm in our daily lives, encouraging both individual and industrial investment in renewable energy. As the world eyes new horizons in clean energy solutions, the research led by HKUST stands as a cornerstone in the burgeoning field of solar technology.

Leave a Reply