The increasing concern over marine pollution, exacerbated by the recent discharge of nuclear wastewater from Japan, has once again pushed the issue of environmental degradation into the spotlight. While various forms of marine pollution exist, oil pollution remains one of the most significant and devastating problems. Oil pollution arises from a multitude of sources, including oil spills, offshore drilling, and leaks from oil pipelines. The detrimental impact of oil spills on marine life and ecosystems cannot be overstated. It suffocates fish, engulfs seabirds’ feathers, and obstructs light from reaching photosynthetic aquatic plants. Furthermore, it wreaks havoc on coral reefs, compromising their delicate balance and vitality. The economic consequences are dire as well, as local tourism and fisheries suffer substantial losses. Addressing this pressing issue calls for the development of effective oil separation techniques that are economically viable and environmentally friendly.
A Novel Approach Utilizing Solar Thermal Energy
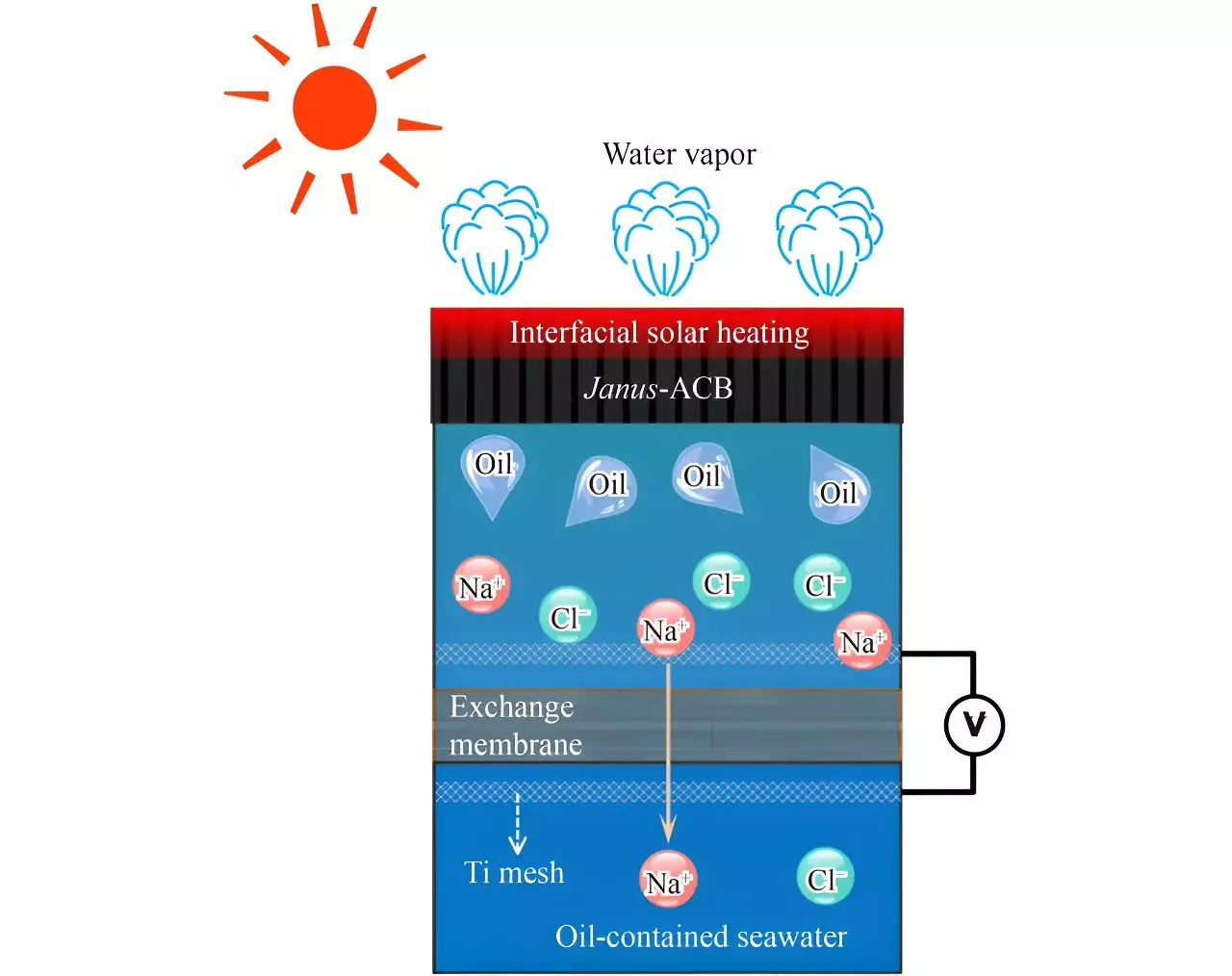
Researchers from China have recently proposed an innovative solution to tackle oil-water mixtures by leveraging the power of solar thermal energy. Unlike conventional protocols that are hindered by poor separation efficiency, high energy consumption, and the risk of secondary pollution, this new approach exhibits significant promise. By harnessing solar energy directly, this method renders minimal environmental impact in separating two-phase mixtures. Moreover, its geographical applicability is not restricted, as it functions effectively on any oil-contaminated seawater surface exposed to sunlight.
Furthermore, this technique boasts additional advantages, including the concurrent generation of electricity, high oil removal efficiency exceeding 99%, and long-term stability. In light of these impressive outcomes, the research team has unveiled an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for extracting resources from oil-contaminated seawater. The secret lies in a remarkably smart design incorporating a wood absorber, which enables both low-cost and environmentally friendly operations. Through carbonization, the wood absorber showcases exceptional light adsorption capability. The utilization of the Janus structure, widely employed in oil/water separation, further enhances the device’s longevity. Even after numerous test cycles, there is no apparent performance degradation.
Promising Results and Future Studies
During standardized tests, the Janus wood absorber demonstrates a remarkable oil removal rate, even when exposed to highly concentrated oily wastewater. Although this breakthrough shows much potential, the research team acknowledges that more comprehensive studies are necessary. Future research endeavors will involve conducting more case studies and considering additional factors that influence the actual process of oil-water separation, such as weather conditions and photothermal conversion performance. While the proposed technique has its merits, the team humbly acknowledges that there is still a long way to go before it can be implemented on a large scale.
The advancement of eco-friendly oil-waste separation techniques utilizing solar thermal energy offers hope amidst the concerning issue of marine pollution. By directly utilizing solar energy, this innovative approach demonstrates efficiency, low environmental impact, and broad geographical applicability. The integration of a wood absorber and the Janus structure showcases the potential for cost-effective and sustainable methods of addressing oil-contaminated seawater. Despite the tremendous progress made by the research team, continuous efforts and further studies are required to refine and optimize this technology. Ultimately, it is through such groundbreaking research that humankind can mitigate the devastating effects of oil pollution and protect our precious marine ecosystems.

Leave a Reply