Fuel cells have long been hailed as a potential game-changer in the quest for clean energy. With the ability to revolutionize transportation and power generation, fuel cells offer a promising source of green energy. These cells produce electricity through a chemical reaction that only results in water and heat as byproducts. However, challenges remain in developing commercially viable fuel cells. Research has predominantly focused on cells that employ platinum as the catalyst, but its scarcity, cost, and instability have posed significant hurdles.
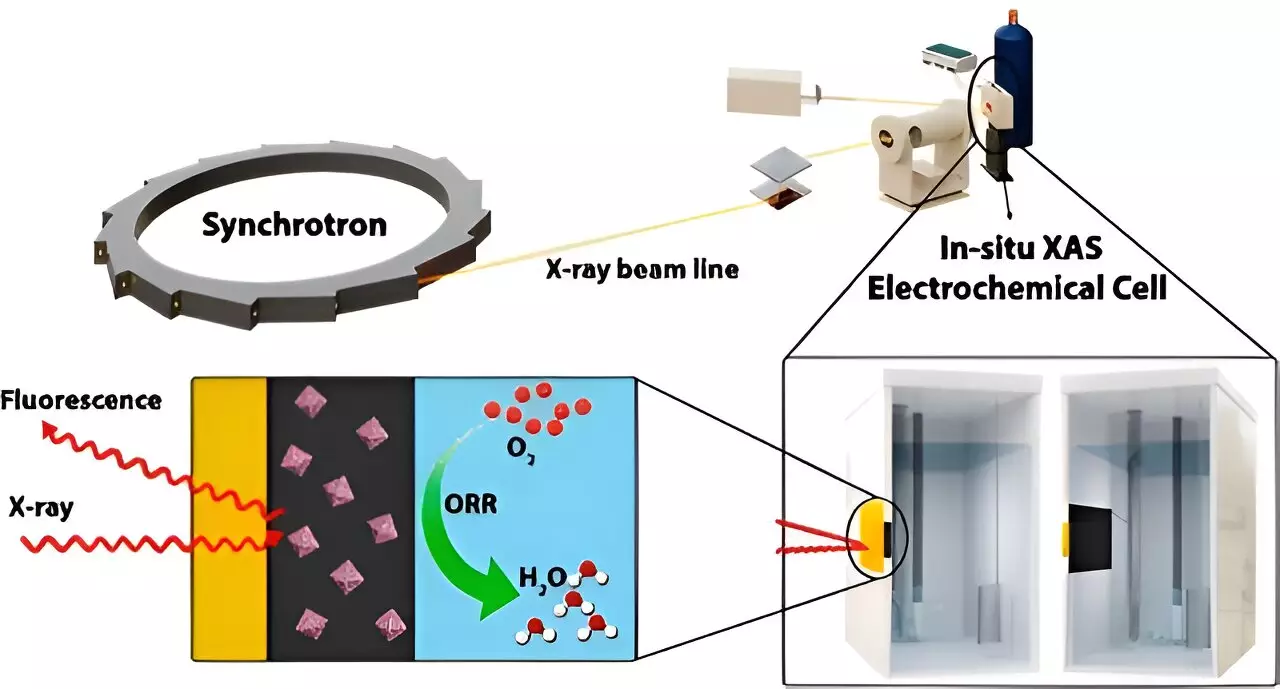
Researchers from Western University have undertaken a notable study to overcome the existing limitations of fuel cells. By integrating other metals, such as palladium and cobalt, with platinum, they have managed to reduce the amount of platinum required for energy production. Additionally, this new catalyst has demonstrated enhanced stability. The team employed the Canadian Light Source at the University of Saskatchewan to develop and test their innovative approach.
The researchers utilized the Canadian Light Source to carry out real-time analysis of the new nanomaterials. This analysis provided essential insights into the binding of oxygen with platinum and the impact of electron transfer between platinum and other metals in the catalyst on its efficiency and performance. Through this method, the team gained valuable knowledge that could lead to further improvements in fuel cell technology.
The integration of palladium and cobalt with platinum has not only enhanced the catalytic performance but has also improved the durability of the catalyst. This breakthrough not only reduces reliance on scarce and expensive materials but also increases the efficiency and lifespan of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). As a result, fuel cells have the potential to become more economically viable and environmentally friendly, driving the broader adoption of clean energy technologies.
The stable results produced in this study bring us closer to realizing sustainable energy solutions. By increasing the efficiency and reducing costs of fuel cells, this research addresses their limitations and paves the way for their wider implementation. Moreover, the improved environmental impact of fuel cells contributes to a greener future.
Fuel cells hold immense potential as a green energy source, but obstacles have hindered their widespread adoption. The integration of palladium and cobalt with platinum represents a significant breakthrough that improves the efficiency and durability of fuel cell catalysts. With this innovative approach, fuel cell technology may become more economically viable and environmentally friendly. The study conducted by the researchers from Western University offers a promising glimpse into the future of clean energy technologies.

Leave a Reply