A recent study conducted by a team of molecular engineers at Tsinghua University in China has pushed the boundaries of hydrogel technology. Traditionally known for their stretchiness, hydrogels have lacked the elasticity to return to their original form after being stretched. However, this new type of hydrogel developed by the Chinese researchers is a game-changer in the field.
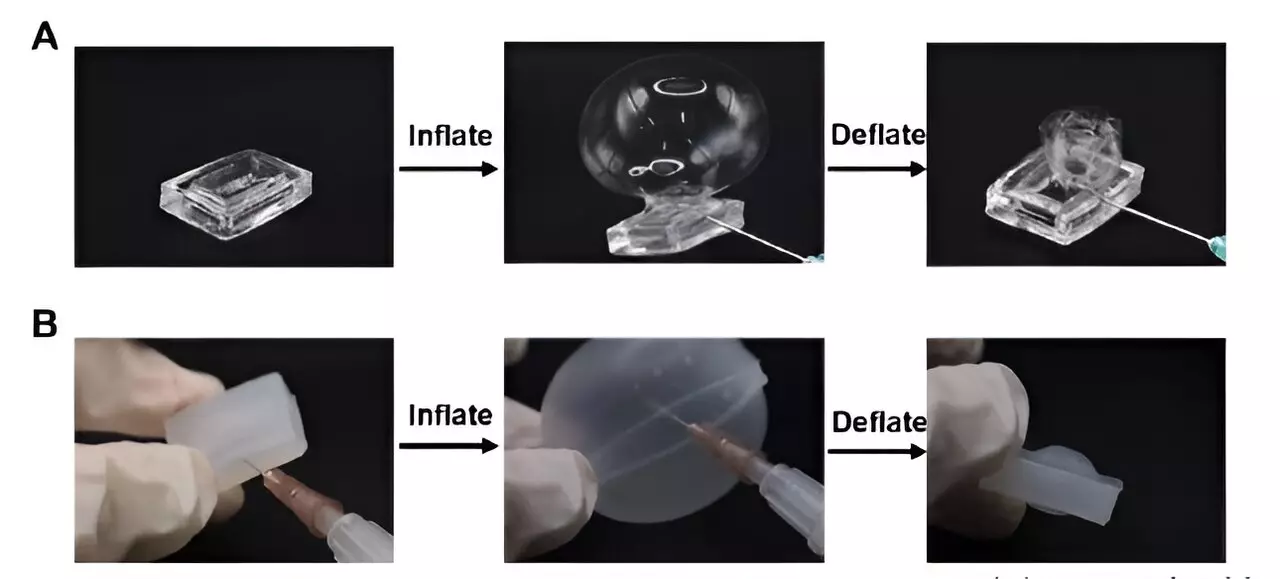
In a departure from the conventional method of creating hydrogels, the research team incorporated “pearl necklace chains” into their design. These polymer chains, shaped like coils and interconnected by carbon atoms, allow the hydrogel to stretch up to 15 times its original size and then snap back to its initial shape effortlessly. By removing water from the hydrogel, causing the existing chains to attach to each other, and then reintroducing water, the team was able to achieve remarkable results.
Implications for Various Industries
The potential applications of this new hydrogel are vast. The researchers demonstrated its effectiveness by building robot grippers capable of handling delicate objects, such as strawberries, without causing any damage. The ability of this hydrogel to stretch in all directions opens up possibilities for its use in fields ranging from biomedicine to robotics. Its commercial applications are bound to be diverse and transformative.
With the development of this highly elastic hydrogel, the world of materials science has taken a significant step forward. The implications of this breakthrough extend beyond the laboratory, offering new opportunities for innovation and progress in multiple industries. As researchers continue to explore the capabilities of this groundbreaking material, the future looks brighter and more resilient than ever before.

Leave a Reply