As the climate pattern known as El Niño begins to decline, researchers have discovered a potential link between the strength of these events and the melting Arctic sea ice. A new study published in Science Advances sheds light on how the interaction between Arctic sea ice and the atmosphere affects the intensity of El Niño events.
The Impact of Arctic Sea Ice on El Niño
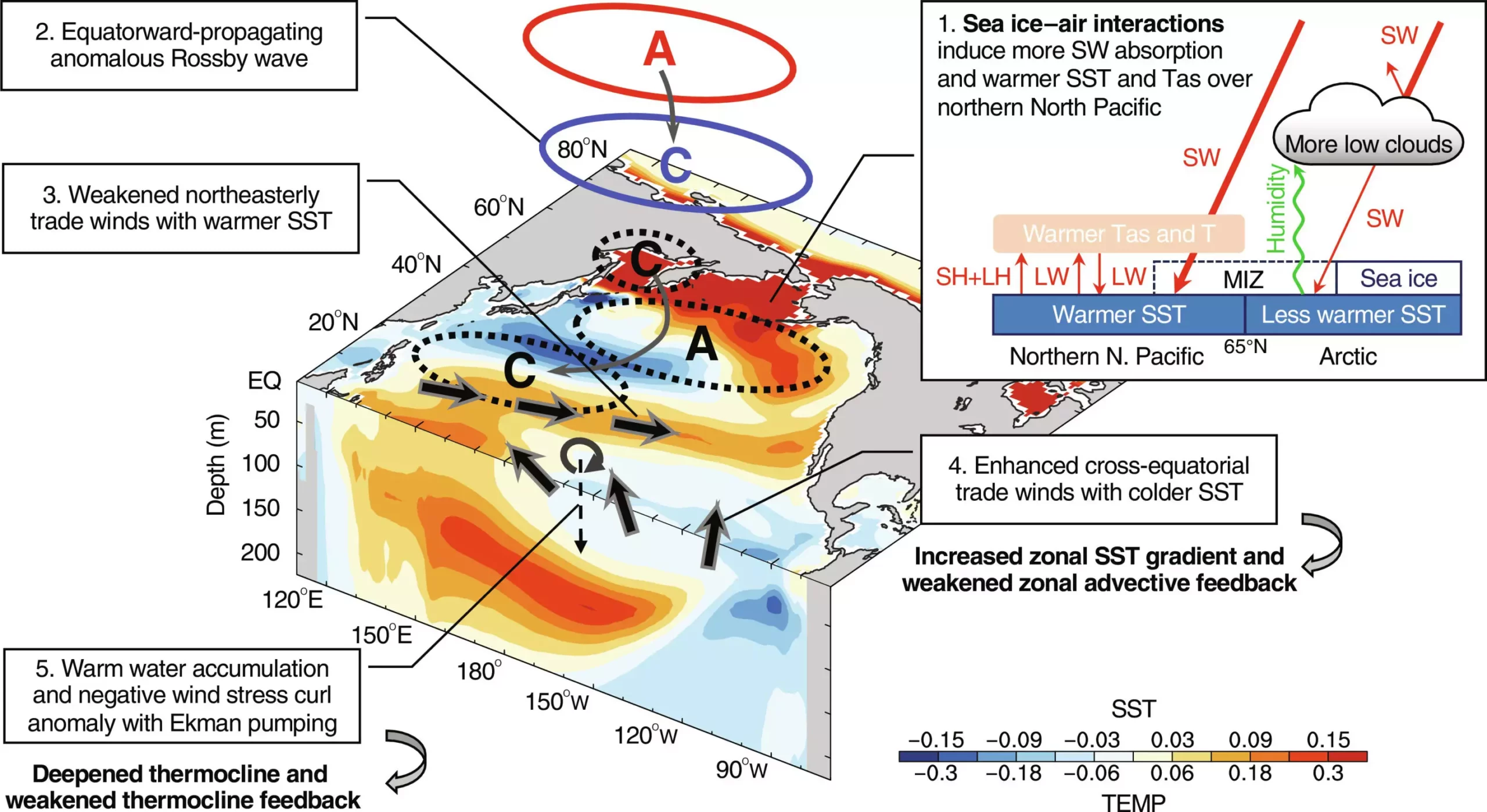
The study, conducted by researchers from the University at Albany and Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, utilized climate model simulations and observational data to analyze the relationship between Arctic sea ice and El Niño. The findings suggest that the current interaction of Arctic sea ice with the atmosphere weakens El Niño events by up to 17%. This reduction in strength is significant and could have far-reaching implications for future climate patterns.
Climate Model Simulations
The researchers performed global climate model simulations over a 500-year period using the Community Earth System Model. By comparing simulations with and without sea ice-air interactions in the Arctic, the researchers were able to determine the impact of Arctic sea ice on El Niño-related variations in the tropical Pacific Ocean. The results showed that the presence of Arctic sea ice-air interactions reduced the strength of El Niño events by 12 to 17%.
Historical observations from two different time periods, one with strong sea ice-air interactions and the other with weak interactions, align with the model results. This consistency reinforces the importance of considering Arctic sea ice in climate models to accurately predict changes in El Niño activity over the tropical Pacific. With projections indicating a rapid decline in Arctic sea ice in the coming decades, the study emphasizes the need for a more realistic representation of sea ice-air interactions in climate models to better understand and project the impacts of El Niño in a warming future.
This study adds to a series of research papers focusing on changes in Arctic climate, with previous work led by the researchers highlighting the causes of Arctic Amplification. The main takeaway from this study is the significant role that shrinking Arctic sea ice plays in influencing climate patterns, including the strength of El Niño events. As global warming continues to affect the Arctic, it is crucial to consider the implications of melting sea ice on our climate and be prepared for potential changes in El Niño activity in the future.
The study’s findings underscore the intricate relationship between Arctic sea ice and El Niño events, highlighting the need for further research and improved modeling techniques to accurately predict and prepare for the impacts of climate change on our planet’s climate system. By understanding the complexities of these interactions, we can work towards developing effective strategies to mitigate the consequences of shrinking Arctic sea ice and the potential for stronger El Niño events in the future.

Leave a Reply