In recent years, the field of cinematography has been revolutionized by advancements in drone technology and camera systems. These developments have enabled filmmakers to capture scenes from unique angles and in higher resolutions than ever before. One such innovation is CineMPC, a fully autonomous cinematographic system developed by researchers at the University of Zaragoza and Stanford University. This system utilizes a drone equipped with a cinematographic camera, allowing it to film multiple targets autonomously while following a director’s instructions. In this article, we will explore the implications of this groundbreaking technology in the film industry and other fields, as well as the potential benefits it brings.
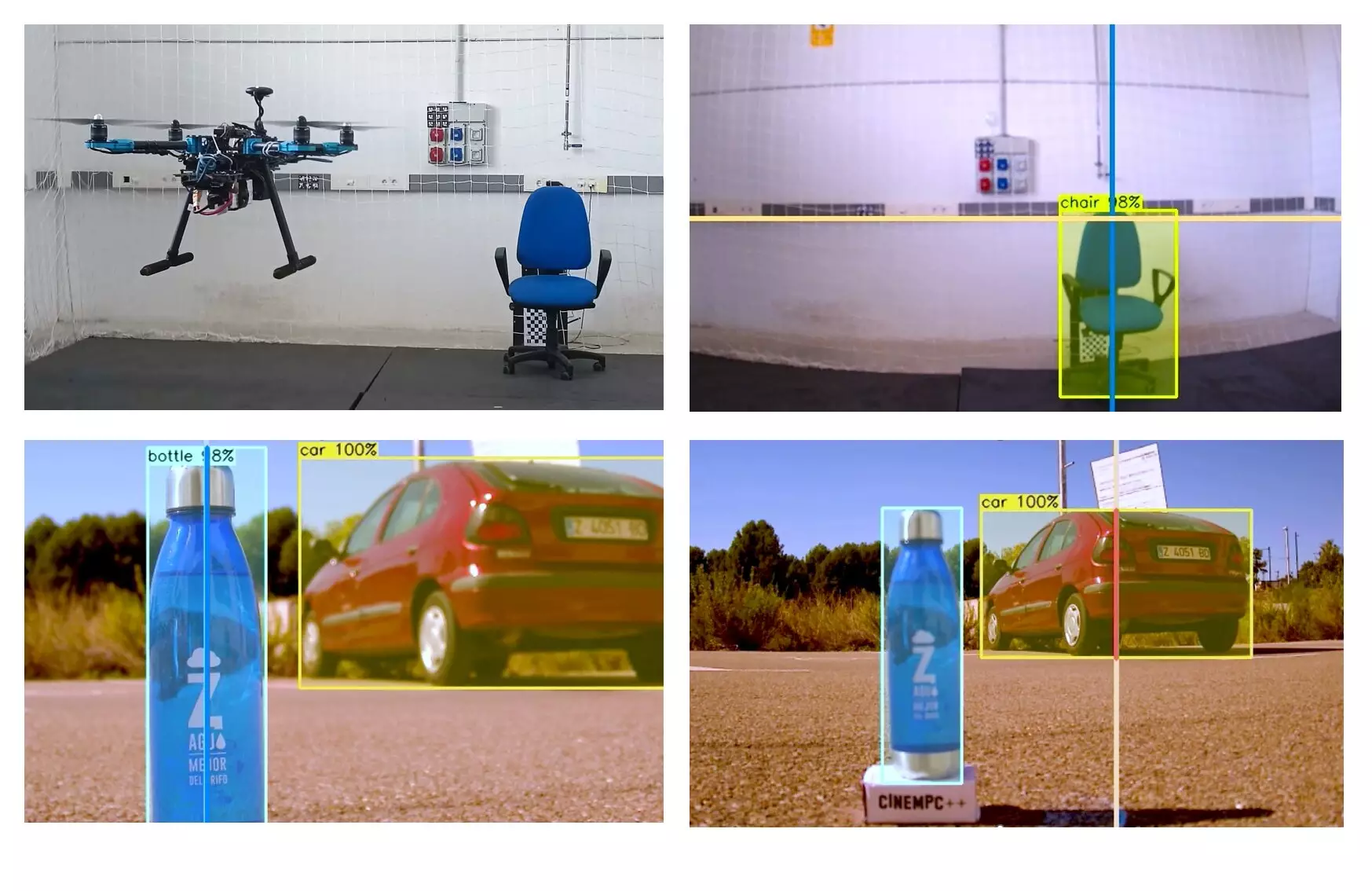
Existing solutions for autonomous drone cinematography have overlooked a crucial aspect: the automatic control over camera intrinsic parameters. These parameters, such as focal length, aperture, and focus distance, are essential in achieving various artistic and technical goals in cinematography. CineMPC fills this gap by autonomously determining the appropriate camera intrinsics to achieve a wide array of user-defined cinematographic instructions. This innovative approach opens up new possibilities for filmmakers, providing them with greater creative freedom and control over their footage.
The researchers behind CineMPC have extensively tested the system to assess its performance in real-world settings. By applying the software to a drone equipped with a controllable professional camera, they were able to film various scenes with remarkable results. CineMPC reliably estimated the relative poses of filmed targets, allowing for precise tracking and unique effects. Filmmakers can now add a personal touch to their shots, creating stunning visuals and enhancing the overall cinematic experience.
While the implications of CineMPC for cinematography are remarkable on their own, the system also holds promise in other fields. For instance, environmental scientists and researchers can use CineMPC to closely monitor wildlife and natural environments without disrupting them. By controlling the zoom of drone-equipped cameras, they can observe animals and plants in their natural habitats from a distance. Similarly, CineMPC can revolutionize precision agriculture by enabling the monitoring of large fields and the close inspection of specific plants. This technology has the potential to increase efficiency and reduce costs in various sectors.
The updated version of CineMPC is readily accessible to developers, cinematographers, and filmmakers online. Its availability is expected to enhance the use of drones in the film industry, enabling filmmakers to capture unique and visually stunning shots. However, the applications of CineMPC extend beyond cinematography. The researchers are actively working on the development of advanced AI techniques to simplify the interaction with the system. Their goal is to democratize the use of autonomous drones by creating user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls. This approach will make it accessible to a wider range of users, further fueling innovation in various industries.
The advancements in autonomous drone cinematography brought by CineMPC have the potential to revolutionize the film industry and other sectors. Filmmakers can now push the boundaries of creativity and storytelling, capturing breathtaking visuals from previously inaccessible angles. Moreover, the applications of this technology extend beyond the entertainment industry. Environmental monitoring, precision agriculture, and research fields can benefit from the capabilities offered by CineMPC. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in autonomous drone systems, opening up new possibilities and reshaping various industries. The future of cinematography is here, driven by innovation and the marriage of technology and art.

Leave a Reply